The effect of AIDS defining conditions on immunological recovery among patients initiating antiretroviral therapy at Joint Clinical Research Centre, Uganda
- PMID: 19630949
- PMCID: PMC2731026
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-6405-6-17
The effect of AIDS defining conditions on immunological recovery among patients initiating antiretroviral therapy at Joint Clinical Research Centre, Uganda
Abstract
Background: Many HIV-infected patients only access health care once they have developed advanced symptomatic disease resulting from AIDS Defining Conditions (ADCs). We carried out a study to establish the effect of ADCs on immunological recovery among patients initiated on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
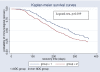
Methods: A retrospective cohort of 427 HIV-1 patients who were initiated on ART between January 2002 and December 2006 was studied. Data on ADCs was retrieved from Joint Clinical Research Centre (JCRC) data base and backed up by chart reviews. We employed Kaplan-Meier survival curves to estimate median time to 50 CD4 cells/microl from the baseline value to indicate a good immunological recovery process. Cox proportional hazard models were used at multivariate analysis.
Results: The median time to gaining 50 CD4 cells/microl from the baseline value after ART initiation was longer in the ADC (9.3 months) compared to the non-ADC group (6.9 months) (log rank test, p = 0.027). At multivariate analysis after adjusting for age, sex, baseline CD4 count, baseline HIV viral load, total lymphocyte count and adherence level, factors that shortened the median time to immunological recovery after ART initiation were belonging to the non-ADC group (HR = 1.31; 95% CI: 1.03-1.28, p = 0.028), adherence to ART of >or= 95% (HR = 2.22; 95% CI: 1.57-3.15, p = 0.001) and a total lymphocyte count >or= 1200 cells/mm3 (HR = 1.84; 95% CI: 1.22-2.78, p = 0.003). A low baseline CD4 count of <or= 200 cells/microl (HR = 0.52; 95% CI: 0.37-0.77, p = 0.001) was associated with a longer time to immunological recovery. There was no interaction between low CD4 counts and ADC group.
Conclusion: Patients with ADCs take longer to regain their CD4 counts due to the defect in the immune system. This may prolong their risk of morbidity and mortality.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in adults and adolescents. recomendations for a public health approach. 2006. http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/artadultguidelines.pdf - PubMed
-
- Amolo-Okero F, Aceng E, Madraa E, Namagala E, Serutoke J. Scaling up antiretroviral Therapy: Experience in Uganda. WHO; 2003. http://www.emro.who.int/aiecf/web46.pdf
-
- Uganda . National Antiretroviral Treatment Guidelines for Adults, Adolescents and Children. Ministry of Health; 2008.
-
- Lawn S, Wood R. How can earlier entry of patients into antiretroviral programs in low-income countries be promoted? Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42 http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/499527?url_ver=Z39.88-2... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lederman HM, Williams PL, Wu JW, Evans TG, Cohn SG, McCutchan JA. Incomplete immune reconstitution after initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with severe CD4+ cell depletion. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:1794–1803. doi: 10.1086/379900. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials