cis-Inhibition of Notch by endogenous Delta biases the outcome of lateral inhibition
- PMID: 19631544
- PMCID: PMC2761761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.042
cis-Inhibition of Notch by endogenous Delta biases the outcome of lateral inhibition
Abstract
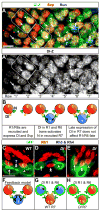
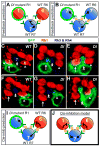
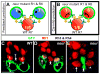
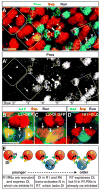
Lateral inhibition mediated by Delta/Notch (Dl/N) signaling is used throughout development to limit the number of initially equivalent cells that adopt a particular fate. Although adjacent cells express both Dl ligand and N receptor, signaling between them ultimately occurs in only one direction. Classically, this has been explained entirely by feedback: activated N can downregulate Dl, amplifying even slight asymmetries in the Dl or N activities of adjacent cells. Here, however, we present an example of lateral inhibition in which unidirectional signaling depends instead on Dl's ability to inhibit N within the same cell, a phenomenon known as cis-inhibition. By genetically manipulating individual R1/R6/R7 photoreceptor precursors in the Drosophila eye, we show that loss of Dl-mediated cis-inhibition reverses the direction of lateral signaling. Based on our finding that Dl in R1/R6s requires endocytosis to trans-activate but not to cis-inhibit N, we reexamine previously published data from other examples of lateral inhibition. We conclude that cis-inhibition generally influences the direction of Dl/N signaling and should therefore be included in standard models of lateral inhibition.
Figures
Comment in
-
Notch signalling: receptor cis-inhibition to achieve directionality.Curr Biol. 2009 Aug 25;19(16):R683-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.025. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19706274
References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Baker NE. Notch signaling in the nervous system. Pieces still missing from the puzzle. Bioessays. 2000;22:264–273. - PubMed
-
- Bray SJ. Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Heitzler P, Simpson P. The choice of cell fate in the epidermis of Drosophila. Cell. 1991;64:1083–1092. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson HA, Fitzgerald K, Greenwald I. Reciprocal changes in expression of the receptor lin-12 and its ligand lag-2 prior to commitment in a C. elegans cell fate decision. Cell. 1994;79:1187–1198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

