Comparing registration methods for mapping brain change using tensor-based morphometry
- PMID: 19631572
- PMCID: PMC2773147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2009.06.002
Comparing registration methods for mapping brain change using tensor-based morphometry
Abstract
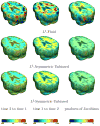
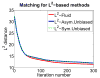
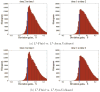
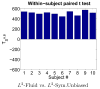
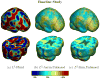
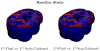
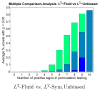
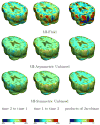
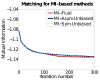
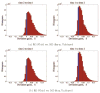
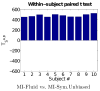
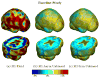
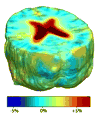
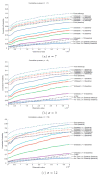
Measures of brain changes can be computed from sequential MRI scans, providing valuable information on disease progression for neuroscientific studies and clinical trials. Tensor-based morphometry (TBM) creates maps of these brain changes, visualizing the 3D profile and rates of tissue growth or atrophy. In this paper, we examine the power of different nonrigid registration models to detect changes in TBM, and their stability when no real changes are present. Specifically, we investigate an asymmetric version of a recently proposed Unbiased registration method, using mutual information as the matching criterion. We compare matching functionals (sum of squared differences and mutual information), as well as large-deformation registration schemes (viscous fluid and inverse-consistent linear elastic registration methods versus Symmetric and Asymmetric Unbiased registration) for detecting changes in serial MRI scans of 10 elderly normal subjects and 10 patients with Alzheimer's Disease scanned at 2-week and 1-year intervals. We also analyzed registration results when matching images corrupted with artificial noise. We demonstrated that the unbiased methods, both symmetric and asymmetric, have higher reproducibility. The unbiased methods were also less likely to detect changes in the absence of any real physiological change. Moreover, they measured biological deformations more accurately by penalizing bias in the corresponding statistical maps.
Figures





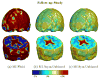

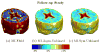
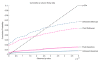
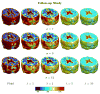
Similar articles
-
Asymmetric and Symmetric Unbiased Image Registration: Statistical Assessment of Performance.Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit Workshops. 2008 Jun;2008:10.1109/CVPRW.2008.4562988. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2008.4562988. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit Workshops. 2008. PMID: 29152411 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical properties of Jacobian maps and the realization of unbiased large-deformation nonlinear image registration.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007 Jun;26(6):822-32. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2007.892646. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17679333
-
Tensor-based morphometry with stationary velocity field diffeomorphic registration: application to ADNI.Neuroimage. 2010 Jul 1;51(3):956-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.061. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20211269 Free PMC article.
-
Nonrigid coregistration of diffusion tensor images using a viscous fluid model and mutual information.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007 Nov;26(11):1598-612. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2007.906786. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 18041274
-
Incorporating DTI data as a constraint in deformation tensor morphometry between T1 MR images.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007;20:223-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-73273-0_19. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17633702 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combining boundary-based methods with tensor-based morphometry in the measurement of longitudinal brain change.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2013 Feb;32(2):223-36. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2012.2220153. Epub 2012 Sep 21. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23014714 Free PMC article.
-
Logical circularity in voxel-based analysis: normalization strategy may induce statistical bias.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Mar;35(3):745-59. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22211. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 23151955 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of registration algorithms in different brain databases with varying difficulty: results and insights.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014 Oct;33(10):2039-65. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2330355. Epub 2014 Jun 13. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24951685 Free PMC article.
-
Gray matter atrophy rate as a marker of disease progression in AD.Neurobiol Aging. 2012 Jul;33(7):1194-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2012. PMID: 21163551 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear registration of longitudinal images and measurement of change in regions of interest.Med Image Anal. 2011 Aug;15(4):489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2011.02.005. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Med Image Anal. 2011. PMID: 21388857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avants B, Gee JC. Geodesic estimation for large deformation anatomical shape averaging and interpolation. NeuroImage. 2004;23 1:S139–50. - PubMed
-
- Beg M, Miller M, Trouve A, Younes L. Computing large deformation metric mappings via geodesic flows of diffeomorphisms. International Journal of Computer Vision. 2005;61(2):139–157.
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B. 1995;57(1):289–300.
-
- Broit C. PhD thesis. University of Pennsylvania; 1981. Optimal registration of deformed images.
-
- Brun C, Lepore N, Pennec X, Chou Y, Lopez O, Aizenstein H, Becker J, Toga A, Thompson P. Comparison of standard and Riemannian elasticity for tensor-based morphometry in HIV/AIDS. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention.2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

