Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats
- PMID: 19631625
- PMCID: PMC2744502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.029
Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats
Abstract
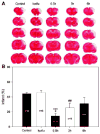
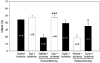
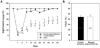
Remote ischemic postconditioning (RIP) refers to an ischemia conducted in a distant organ that protects against a prior ischemia in another organ. We tested whether RIP protects against focal ischemia in the rat brain. Stroke was generated by a permanent occlusion of the left distal middle cerebral artery combined with a 30-min occlusion of the bilateral common carotid arteries (CCA) in male rats. After CCA release, RIP was generated by three cycles of 15-min occlusion/15-min release of the left-hind femoral artery. The results showed that rapid RIP performed immediately after CCA release reduced infarction by 67% measured at 2 days after stroke. In addition, delayed RIP initiated as late as 3 h, but not 6 h, still robustly reduced infarction by 43% 2 days after stroke. RIP's protective effect was abolished by injecting the protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide, and the afferent nerve blocker, capsaicin, suggesting that RIP blocks ischemic injury by modulating protein synthesis and nerve activity. Nevertheless, rapid RIP did not reduce infarction size 2 months after stroke while it ameliorated the outcome of the behavioral test. In conclusion, RIP attenuates brain injury after focal ischemia.
Figures

References
-
- Barone FC, White RF, Spera PA, Ellison J, Currie RW, Wang X, Feuerstein GZ. Ischemic preconditioning and brain tolerance: temporal histological and functional outcomes, protein synthesis requirement, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and early gene expression. Stroke. 1998;29:1937–1950. discussion 1950-1931. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski T, Konturek PC, Konturek SJ, Pajdo R, Kwiecien S, Pawlik M, Drozdowicz D, Sliwowski Z, Pawlik WW. Ischemic preconditioning of remote organs attenuates gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury through involvement of prostaglandins and sensory nerves. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;499:201–213. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski T, Konturek PC, Pajdo R, Kwiecien S, Sliwowski Z, Drozdowicz D, Ptak-Belowska A, Pawlik M, Konturek SJ, Pawlik WW, Hahn GG. Importance of brain-gut axis in the gastroprotection induced by gastric and remote preconditioning. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004;55:165–177. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich WD, Busto R, Alonso O, Globus MY, Ginsberg MD. Intraischemic but not postischemic brain hypothermia protects chronically following global forebrain ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:541–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

