Functional study of the P32T ITPA variant associated with drug sensitivity in humans
- PMID: 19631656
- PMCID: PMC2745931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.051
Functional study of the P32T ITPA variant associated with drug sensitivity in humans
Abstract
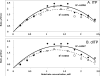
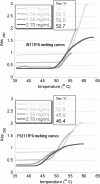
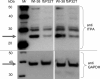
Sanitization of the cellular nucleotide pools from mutagenic base analogues is necessary for the accuracy of transcription and replication of genetic material and plays a substantial role in cancer prevention. The undesirable mutagenic, recombinogenic, and toxic incorporation of purine base analogues [i.e., ITP, dITP, XTP, dXTP, or 6-hydroxylaminopurine (HAP) deoxynucleoside triphosphate] into nucleic acids is prevented by inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA). The ITPA gene is a highly conserved, moderately expressed gene. Defects in ITPA orthologs in model organisms cause severe sensitivity to HAP and chromosome fragmentation. A human polymorphic allele, 94C-->A, encodes for the enzyme with a P32T amino acid change and leads to accumulation of non-hydrolyzed ITP. ITPase activity is not detected in erythrocytes of these patients. The P32T polymorphism has also been associated with adverse sensitivity to purine base analogue drugs. We have found that the ITPA-P32T mutant is a dimer in solution, as is wild-type ITPA, and has normal ITPA activity in vitro, but the melting point of ITPA-P32T is 5 degrees C lower than that of wild-type. ITPA-P32T is also fully functional in vivo in model organisms as determined by a HAP mutagenesis assay and its complementation of a bacterial ITPA defect. The amount of ITPA protein detected by Western blot is severely diminished in a human fibroblast cell line with the 94C-->A change. We propose that the P32T mutation exerts its effect in certain human tissues by cumulative effects of destabilization of transcripts, protein stability, and availability.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Elevated Levels of DNA Strand Breaks Induced by a Base Analog in the Human Cell Line with the P32T ITPA Variant.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Sep 26;2010:872180. doi: 10.4061/2010/872180. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20936128 Free PMC article.
-
The human ITPA polymorphic variant P32T is destabilized by the unpacking of the hydrophobic core.J Struct Biol. 2013 Jun;182(3):197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Mar 23. J Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23528839 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative in vitro and in vivo characterization of the human P32T mutant ITPase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Feb;1802(2):269-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19914375 Free PMC article.
-
ITPA (inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase): from surveillance of nucleotide pools to human disease and pharmacogenetics.Mutat Res. 2013 Oct-Dec;753(2):131-146. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23969025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inosine Triphosphate Pyrophosphatase (ITPase): Functions, Mutations, Polymorphisms and Its Impact on Cancer Therapies.Cells. 2022 Jan 24;11(3):384. doi: 10.3390/cells11030384. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between ITPA rs1127354 polymorphisms and efficacy of antiviral treatment in Northeast Chinese CHC patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(29):e7554. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007554. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28723780 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase in maintaining genome stability and the prevention of apoptosis in human cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032313. Epub 2012 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384212 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Levels of DNA Strand Breaks Induced by a Base Analog in the Human Cell Line with the P32T ITPA Variant.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Sep 26;2010:872180. doi: 10.4061/2010/872180. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20936128 Free PMC article.
-
Variant Inosine Triphosphatase Phenotypes Are Associated With Increased Ribavirin Triphosphate Levels.J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;57(1):118-124. doi: 10.1002/jcph.783. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27349952 Free PMC article.
-
The human ITPA polymorphic variant P32T is destabilized by the unpacking of the hydrophobic core.J Struct Biol. 2013 Jun;182(3):197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Mar 23. J Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23528839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones EW, Fink G. Regulation of amino acid and nucleotide biosynthesis in yeast. In: N. SJ, W. JE, R BJ, editors. Molecular biology of the yeast Saccharomyces. Metabolism and gene expression. Cold Spring Harbor Press; Cold Spring Harbor: 1982. pp. 181–299.
-
- Zalkin H, Nygaard P. Biosynthesis of purine nucleotides. In: Neidhardt FC, editor. Escherichia coli and Salmonella, cellular and molecular biology. ASM press; Washington DC: 1996. pp. 561–579.
-
- Bradshaw JS, Kuzminov A. RdgB acts to avoid chromosome fragmentation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2003;48:1711–25. - PubMed
-
- Emerit I, Filipe P, Meunier P, Auclair C, Freitas J, Deroussent A, Gouyette A, Fernandes A. Clastogenic activity in the plasma of scleroderma patients: a biomarker of oxidative stress. Dermatology. 1997;194:140–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

