Characterization of the ovarian and reproductive abnormalities in prepubertal and adult estrogen non-responsive estrogen receptor alpha knock-in (ENERKI) mice
- PMID: 19631674
- PMCID: PMC2752961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2009.06.012
Characterization of the ovarian and reproductive abnormalities in prepubertal and adult estrogen non-responsive estrogen receptor alpha knock-in (ENERKI) mice
Abstract
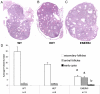
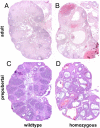
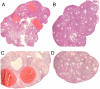
Estrogen non-responsive estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) knock-in (ENERKI) mice have a mutation (glycine 525 to leucine, G525L) in the ligand-binding domain of ERalpha. The mutant ERalpha protein has a significantly lower affinity and response to endogenous estrogens, while not altering growth factor activated ligand-independent pathways. ENERKI females demonstrated signs of early follicle development as determined by a significant increase in antral follicle formation by 20 days of age. Adult ENERKI females were infertile, had hemorrhagic ovarian follicular cysts, and failed to develop corpora lutea in response to a superovulation regimen. These results illustrate the importance of ERalpha ligand-induced signaling for ovarian development and for estrogen feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary. Although ERalpha ligand-induced signaling by endogenous estrogens is lost in ENERKI females, the ERalpha selective agonist propyl pyrazole triol (PPT), a synthetic nonsteroidal compound, is still able to activate G525L ERalphain vivo to increase uterine weight. To test whether PPT could restore ligand-dependent receptor activation, ENERKI females were treated with PPT and evaluated for spontaneous ovulation, ovarian hemorrhagic cysts, and LH serum levels. Daily PPT treatments beginning on day 4 of life prevented formation of ovarian hemorrhagic cysts in adult ENERKI animals. In accordance with this result, preputial gland weight and LH levels were also lowered in these animals, indicating PPT treatments most likely led to restoration of ERalpha negative feedback of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Figures
References
-
- Klinge CM. Estrogen receptor interaction with co-activators and co-repressors. Steroids. 2000;65:227–51. - PubMed
-
- Manolagas SC, Kousteni S. Perspective: nonreproductive sites of action of reproductive hormones. Endocrinology. 2001;142:2200–4. - PubMed
-
- Hall JM, Couse JF, Korach KS. The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36869–72. - PubMed
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev. 1999;20:358–417. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, Inoue S. Estrogen receptors: how do they control reproductive and nonreproductive functions? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;270:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

