Bombesin enhances TGF-beta growth inhibitory effect through apoptosis induction in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 19631696
- PMCID: PMC3894738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.07.010
Bombesin enhances TGF-beta growth inhibitory effect through apoptosis induction in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
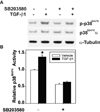
Mammalian intestinal epithelium undergoes continuous cell turn over, with cell proliferation in the crypts and apoptosis in the villus. Both transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta and gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) are involved in the regulation of intestinal epithelial cells for division, differentiation, adhesion, migration and death. Previously, we have shown that TGF-beta and bombesin (BBS) synergistically induce cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and subsequent prostaglandin E(2) (PGE2) production through p38(MAPK) in rat intestinal epithelial cell line stably transfected with GRP receptor (RIE/GRPR), suggesting the interaction between TGF-beta signaling pathway and GRPR. The current study examined the biological responses of RIE/GRPR cells to TGF-beta and BBS. Treatment with TGF-beta1 (40 pM) and BBS (100 nM) together synergistically inhibited RIE/GRPR growth and induced apoptosis. Pretreatment with SB203580 (10 microM), a specific inhibitor of p38(MAPK), partially blocked the synergistic effect of TGF-beta and BBS on apoptosis. In conclusion, BBS enhanced TGF-beta growth inhibitory effect through apoptosis induction, which is at least partially mediated by p38(MAPK).
Figures




References
-
- Babyatsky MW, Podolsky DK. Growth and development in the gastrointestinal tract. In: Yamada T, Alpers DH, Owyang C, Powell DW, editors. Text book of Gastroenterology. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Co.; 1991. pp. 475–501.
-
- Ko TC, Bresnahan WA, Thompson EA. Intestinal cell cycle regulation. In: Meijer L, Guidet S, Philippe M, editors. Progress in Cell Cycle Research. New York: Plenum; 1997. pp. 43–52. - PubMed
-
- Cairnie AB, Lamerton LF, Steel GG. Cell proliferation studies in the intestinal epithelium of the rat. I. Determination of the kinetic parameters. Exp Cell Res. 1965;39:528–538. - PubMed
-
- Potten CS, Wilson JW, Booth C. Regulation and significance of apoptosis in the stem cells of the gastrointestinal epithelium. Stem Cells. 1997;15:82–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

