Formins and microtubules
- PMID: 19631698
- PMCID: PMC2856479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.07.006
Formins and microtubules
Abstract
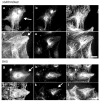
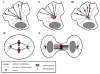
Formins have recently been recognized as prominent regulators of the microtubule (MT) cytoskeleton where they modulate the dynamics of selected MTs in interphase and mitosis. The association of formins with the MT cytoskeleton and their action on MT dynamics are relatively unexplored areas, yet growing evidence supports a direct role in their regulation of MT stability independent of their activity on actin. Formins regulate MT stability alone or in combination with accessory MT binding proteins that have previously been implicated in the stabilization of MTs downstream of polarity cues. As actin and MT arrays are typically remodeled downstream of signaling pathways that orchestrate cell shape and division, formins are emerging as excellent candidates for coordinating the responses of the cytoskeletal in diverse regulated and homeostatic processes.
Figures


References
-
- Downing KH, Nogales E. Tubulin and microtubule structure. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10(1):16–22. - PubMed
-
- Downing KH, Nogales E. New insights into microtubule structure and function from the atomic model of tubulin. Eur Biophys J. 1998;27(5):431–6. - PubMed
-
- Nogales E, Wolf SG, Downing KH. Structure of the alpha beta tubulin dimer by electron crystallography. Nature. 1998;391(6663):199–203. - PubMed
-
- Nogales E, et al. High-resolution model of the microtubule. Cell. 1999;96(1):79–88. - PubMed
-
- Mitchison T, Kirschner M. Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature. 1984;312(5991):237–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

