Mass spectrometry identifies multiple organophosphorylated sites on tubulin
- PMID: 19632257
- PMCID: PMC2753752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.020
Mass spectrometry identifies multiple organophosphorylated sites on tubulin
Abstract
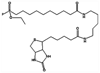
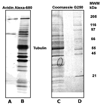
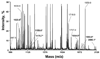
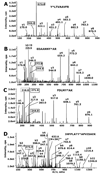
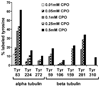
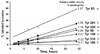
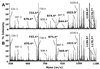
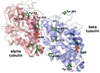
Acute toxicity of organophosphorus poisons (OP) is explained by inhibition of acetylcholinesterase in nerve synapses. Low-dose effects are hypothesized to result from modification of other proteins, whose identity is not yet established. The goal of the present work was to obtain information that would make it possible to identify tubulin as a target of OP exposure. Tubulin was selected for study because live mice injected with a nontoxic dose of a biotinylated organophosphorus agent appeared to have OP-labeled tubulin in brain as determined by binding to avidin beads and mass spectrometry. The experiments with live mice were not conclusive because binding to avidin beads could be nonspecific. To be convincing, it is necessary to find and characterize the OP-labeled tubulin peptide. The search for OP-labeled tubulin peptides was begun by identifying residues capable of making a covalent bond with OP. Pure bovine tubulin (0.012 mM) was treated with 0.01-0.5 mM chlorpyrifos oxon for 24 h at 37 degrees C in pH 8.3 buffer. The identity of labeled amino acids and percent labeling was determined by mass spectrometry. Chlorpyrifos oxon bound covalently to tyrosines 83, 103, 108, 161, 224, 262, 272, 357, and 399 in bovine alpha tubulin, and to tyrosines 50, 51, 59, 106, 159, 281, 310, and 340 in bovine beta tubulin. The most reactive were tyrosine 83 in alpha and tyrosine 281 in beta tubulin. In the presence of 1 mM GTP, percent labeling increased 2-fold. Based on the crystal structure of the tubulin heterodimer (PDB 1jff) tyrosines 83 and 281 are well exposed to solvent. In conclusion seventeen tyrosines in tubulin have the potential to covalently bind chlorpyrifos oxon. These results will be useful when searching for OP-labeled tubulin in live animals.
Figures
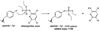
References
-
- Abou-Donia MB. Involvement of cytoskeletal proteins in the mechanisms of organophosphorus ester-induced delayed neurotoxicity. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995;22:358–359. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Donia MB. Organophosphorus ester-induced chronic neurotoxicity. Arch Environ Health. 2003;58:484–497. - PubMed
-
- Adams TK, Capacio BR, Smith JR, Whalley CE, Korte WD. The application of the fluoride reactivation process to the detection of sarin and soman nerve agent exposures in biological samples. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2004;27:77–91. - PubMed
-
- Azaroff LS. Biomarkers of exposure to organophosphorous insecticides among farmers' families in rural El Salvador: factors associated with exposure. Environ Res. 1999;80:138–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

