On-line plasticity in spoken sentence comprehension: Adapting to time-compressed speech
- PMID: 19632341
- PMCID: PMC2775905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.032
On-line plasticity in spoken sentence comprehension: Adapting to time-compressed speech
Abstract
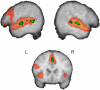
Listeners show remarkable flexibility in processing variation in speech signal. One striking example is the ease with which they adapt to novel speech distortions such as listening to someone with a foreign accent. Behavioural studies suggest that significant improvements in comprehension occur rapidly--often within 10-20 sentences. In the present experiment, we investigate the neural changes underlying on-line adaptation to distorted speech using time-compressed speech. Listeners performed a sentence verification task on normal-speed and time-compressed sentences while their neural responses were recorded using fMRI. The results showed that rapid learning of the time-compressed speech occurred during presentation of the first block of 16 sentences and was associated with increased activation in left and right auditory association cortices and in left ventral premotor cortex. These findings suggest that the ability to adapt to a distorted speech signal may, in part, rely on mapping novel acoustic patterns onto existing articulatory motor plans, consistent with the idea that speech perception involves integrating multi-modal information including auditory and motoric cues.
Figures



References
-
- Adank P., Evans B.G., Stuart-Smith J., Scott S.K. Familiarity with a regional accent facilitates comprehension of that accent in noise. J. Exp. Psychol.: Hum. Percept. Perform. 2009;35:520–529. - PubMed
-
- Aydelott J., Bates E. Effects of acoustic distortion and semantic context on lexical access. Lang. Cogn. Proc. 2004;19:29–56.
-
- Baddeley, A.D., Emslie, H., Nimmo-Smith, I., 1992. The Speed and Capacity of Language Processing (SCOLP) Test.
-
- Bandettini P.A., Jesmanowicz A., van Kylen J., Birn R.M., Hyde J.S. Functional MRI of brain activation induced by scanner acoustic noise. Magn. Reson. Med. 1998;39:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Barbas H., Pandya D.N. Architecture and frontal cortical connections of the premotor cortex (area 6) in the rhesus monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987;256:211–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

