Do management strategies for coronary artery disease influence 6-year cognitive outcomes?
- PMID: 19632391
- PMCID: PMC2753795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.04.061
Do management strategies for coronary artery disease influence 6-year cognitive outcomes?
Abstract
Background: Previous uncontrolled studies have suggested that there is late cognitive decline after coronary artery bypass grafting that may be attributable to use of the cardiopulmonary bypass pump.
Methods: In this prospective, nonrandomized, longitudinal study, we compared cognitive outcomes after on-pump coronary artery bypass surgery (n = 152) with off-pump bypass surgery patients (n = 75); nonsurgical cardiac comparison subjects (n = 99); and 69 heart-healthy comparison (HHC) subjects. The primary outcome measure was change from baseline to 72 months in the following cognitive domains: verbal memory, visual memory, visuoconstruction, language, motor speed, psychomotor speed, attention, executive function, and a composite global score.
Results: There were no consistent differences in 72-month cognitive outcomes among the three groups with coronary artery disease (CAD). The CAD groups had lower baseline performance, and a greater degree of decline compared with HHC. The degree of change was small, with none of the groups having more than 0.5 SD decline. None of the groups was substantially worse at 72 months compared with baseline.
Conclusions: Compared with subjects with no vascular disease risk factors, the CAD patients had lower baseline cognitive performance and greater degrees of decline over 72 months, suggesting that in these patients, vascular disease may have an impact on cognitive performance. We found no significant differences in the long-term cognitive outcomes among patients with various CAD therapies, indicating that management strategy for CAD is not an important determinant of long-term cognitive outcomes.
Figures
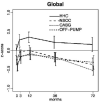
Comment in
-
Invited commentary.Ann Thorac Surg. 2009 Aug;88(2):454. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.05.034. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19632392 No abstract available.
References
-
- Selnes OA, Grega MA, Borowicz LM, Jr., Royall RM, McKhann GM, Baumgartner WA. Cognitive changes with coronary artery disease: a prospective study of coronary artery bypass graft patients and nonsurgical controls. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:1377–1384. - PubMed
-
- Newman MF, Kirchner JL, Phillips-Bute B, et al. Longitudinal assessment of neurocognitive function after coronary- artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Jensen BO, Hughes P, Rasmussen LS, Pedersen PU, Steinbruchel DA. Cognitive outcomes in elderly high-risk patients after off-pump versus conventional coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized trial. Circulation. 2006;113:2790–2795. - PubMed
-
- van Dijk D, Spoor M, Hijman R, et al. Cognitive and cardiac outcomes 5 years after off-pump vs on-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery. JAMA. 2007;297:701–708. - PubMed
-
- Takagi H, Tanabashi T, Kawai N, Umemoto T. Cognitive decline after off-pump versus on-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134:512–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

