7-year trajectories of Alcoholics Anonymous attendance and associations with treatment
- PMID: 19632789
- PMCID: PMC2739250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.06.015
7-year trajectories of Alcoholics Anonymous attendance and associations with treatment
Abstract
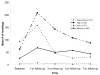
Although many members of Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) are introduced to AA during treatment, the relationship between treatment and AA attendance over time is unknown. This paper describes four latent classes of AA attendance among 586 dependent alcoholics interviewed by telephone 1, 3, 5 and 7 years after baseline, and models the relationship between treatment exposure and AA attendance in each class. There was a low AA group (averaging fewer than 5 meetings at most follow-ups), a medium AA group (about 50 meetings a year at each follow-up), a descending AA group (about 150 meetings year 1, then decreasing steeply), and a high AA group (about 200 meetings at 1 year, then decreasing gradually by year 7). Declines in meeting attendance were not always accompanied by decreases in abstinence. After accounting for the effect of time on AA attendance (i.e., the "ups-and-downs" that occur over time), treatment exposure was minimally related to AA attendance in all but the descending AA group, where it was negatively associated (p<0.001). Considering AA patterns over time highlights a different role for treatment in AA attendance than what is gleaned from analyses at single timepoints.
Figures
References
-
- A.A. World Services. Alcoholics Anonymous 2007 Membership Survey. New York, NY: A.A. World Services; 2008.
-
- Alcoholics Anonymous. Alcoholics Anonymous 1998 Membership Survey. New York, NY: Alcoholics Anonymous; 2001.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Text Revision [DSM-IV-TR] 4. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Caetano R, Raspberry K. Drinking and DSM-IV alcohol and drug dependence among white and Mexican American DUI offenders. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 2000;61(3):420–426. - PubMed
-
- Clark WB, Hilton ME, editors. Alcohol in America: drinking practices and problems. Albany, NY: State University of New York Press; 1991.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical