Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway
- PMID: 19632948
- PMCID: PMC2758558
- DOI: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway
Abstract
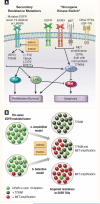
Most advanced non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) with activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations (exon 19 deletions or L858R) initially respond to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) gefitinib and erlotinib. However, over time (median of 6-12 months), most tumors develop acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs. Intense research in these NSCLCs has identified two major mechanisms of resistance to gefitinib/erlotinib: secondary resistance mutations and "oncogene kinase switch" systems. The secondary T790M mutation occurs in 50% of EGFR-mutated patients with TKI resistance, and in vitro, this mutation negates the hypersensitivity of activating EGFR mutations. Sensitive detection methods have identified a proportion of TKI-naive tumors that carry T790M, and these resistant clones may be selected after exposure to gefitinib or erlotinib. Other secondary resistance mutations (D761Y, L747S, T854A) seem to be rare. The amplification of the MET oncogene is present in 20% of TKI-resistant tumors; however, in half of the cases with this "oncogene kinase switch" mechanism the T790M is coexistent. It is possible that other kinases (such as insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor [IGF-1R]) might also be selected to bypass EGFR pathways in resistant tumors. The growing preclinical data in EGFR-mutated NSCLCs with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib has spawned the initiation or conception of clinical trials testing novel EGFR inhibitors that in vitro inhibit T790M (neratinib, XL647, BIBW 2992, and PF-00299804), MET, or IGF-1R inhibitors in combination with EGFR TKIs, and heat shock protein 90 inhibitors. Ongoing preclinical and clinical research in EGFR-mutated NSCLC has the potential to significantly improve the outcomes of patients with these somatic mutations.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2542–50. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, et al. Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2095–103. - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

