Cell cycle actions of parathyroid hormone-related protein in non-small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 19633068
- PMCID: PMC2770787
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90560.2008
Cell cycle actions of parathyroid hormone-related protein in non-small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), a paraneoplastic protein expressed by two-thirds of human non-small cell lung cancers, has been reported to slow progression of lung carcinomas in mouse models and to lengthen survival of patients with lung cancer. This study investigated the effects of ectopic expression of PTHrP on proliferation and cell cycle progression of two human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines that are normally PTHrP negative. Stable transfection with PTHrP decreased H1944 cell DNA synthesis, measured by thymidine incorporation, bromodeoxyuridine uptake, and MTT proliferation assay. A substantial fraction of PTHrP-positive cells was arrested in or slowly progressing through G1. Cyclin D2 and cyclin A2 protein levels were 60-70% lower in PTHrP-expressing cells compared with control cells (P < 0.05, N = 3 independent clones per group), while expression of p27(Kip1), a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, was increased by 35 +/- 9% (mean +/- SE, P < 0.05) in the presence of PTHrP. Expression of other cyclins, including cyclins D1 and D3, and cyclin-dependent kinases was unaffected by PTHrP. PTHrP did not alter the phosphorylation state of Rb, but decreased cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2-cyclin A2 complex formation. Ectopic expression of PTHrP stimulated ERK phosphorylation. In MV522 cells, PTHrP had similar effects on DNA synthesis, cyclin A2 expression, pRb levels, CDK2-cyclin A2 association, and ERK activation. In summary, PTHrP appears to slow progression of lung cancer cells into S phase, possibly by decreasing activation of CDK2. Slower cancer cell proliferation could contribute to slower tumor progression and increased survival of patients with PTHrP-positive lung cancer.
Figures
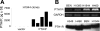
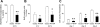
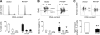
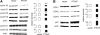
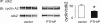
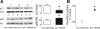
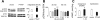
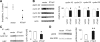
References
-
- Abou-Samra AB, Juppner H, Force T, Freeman MW, Kong XF, Schipani E, Urena P, Richards J, Bonventre JV, Potts JJ, et al. Expression cloning of a common receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide from rat osteoblast-like cells: a single receptor stimulates intracellular accumulation of both cAMP and inositol trisphosphates and increases intracellular free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 2732–2736, 1992 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brandt DW, Wachsman W, Deftos LJ. Parathyroid hormone-like protein: alternative messenger RNA splicing pathways in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 54: 850–853, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Clark JA, Black AR, Leontieva OV, Frey MR, Pysz MA, Kunneva L, Wolszynska-Read A, Roy D, and Black JD. Involvement of the ERK signaling cascased in protein kinase C-mediated cell cycle arrest in intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 279: 9233–9247, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Datta NS, Chen C, Berry JE, McCauley LK. PTHrP signaling targets cyclin D1 and induces osteoblastic cell growth arrest. J Bone Miner Res 20: 1051–1064, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ditmer LS, Burton DW, Deftos LJ. Elimination of the carboxy-terminal sequences of parathyroid hormone-related protein 1-173 increases production and secretion of the truncated forms. Endocrinology 137: 1608–1617, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

