Participation of regulator AscG of the beta-glucoside utilization operon in regulation of the propionate catabolism operon
- PMID: 19633077
- PMCID: PMC2747900
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00663-09
Participation of regulator AscG of the beta-glucoside utilization operon in regulation of the propionate catabolism operon
Abstract
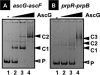
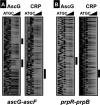
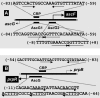
The asc operon of Escherichia coli is one of the cryptic genetic systems for beta-D-galactoside utilization as a carbon source. The ascFB genes for beta-D-galactoside transport and catabolism are repressed by the AscG regulator. After genomic SELEX screening, AscG was found to recognize and bind the consensus palindromic sequence TGAAACC-GGTTTCA. AscG binding was detected at two sites upstream of the ascFB promoter and at three sites upstream of the prpBC operon for propionate catabolism. In an ascG-disrupted mutant, transcription of ascFB was enhanced, in agreement with the repressor model of AscG. This repression was indicated to be due to interference of binding of cyclic AMP-CRP to the CRP box, which overlaps with the AscG-binding site 1, as well as binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. Under conditions of steady-state E. coli growth in a rich medium, the intracellular level of AscG stayed constant at a level supposedly leading to tight repression of the ascFB operon. The level of prpR, encoding the activator of prpBCDE, was also increased in the absence of AscG, indicating the involvement of AscG in repression of prpR. Taken together, these data suggest a metabolic link through interplay between the asc and prp operons.
Figures





References
-
- deCrombrugghe, B., S. Busby, and H. Buc. 1984. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science 224:831-838. - PubMed
-
- Ellington, A. D., and J. W. Szostak. 1990. In vitro selection of DNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818-822. - PubMed
-
- Hall, B. G., and L. Xu. 1992. Nucleotide sequence, function, activation, and evolution of the cryptic asc operon of Escherichia coli K12. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9:688-706. - PubMed
-
- Hall, B. G., S. Yokoyama, and D. H. Calhoun. 1983. Role of cryptic genes in microbial evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1:109-124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

