Processing and stability of inducibly expressed rpsO mRNA derivatives in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 19633085
- PMCID: PMC2737947
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00740-09
Processing and stability of inducibly expressed rpsO mRNA derivatives in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
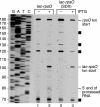
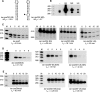
The Bacillus subtilis rpsO gene specifies a small (388-nucleotide), monocistronic mRNA that encodes ribosomal protein S15. We showed earlier that rpsO mRNA decay intermediates accumulated to a high level in a strain lacking polynucleotide phosphorylase. Here, we used inducibly expressed derivatives of rpsO, encoding smaller RNAs that had the complex 5' region deleted, to study aspects of mRNA processing in B. subtilis. An IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside)-inducible rpsO transcript that contained lac sequences at the 5' end, called lac-rpsO RNA, was shown to undergo processing to result in an RNA that was 24 nucleotides shorter than full length. Such processing was dependent on the presence of an accessible 5' terminus; a lac-rpsO RNA that contained a strong stem-loop at the 5' end was not processed and was extremely stable. Interestingly, this stability depended also on ribosome binding to a nearby Shine-Dalgarno sequence but was independent of downstream translation. Either RNase J1 or RNase J2 was capable of processing lac-rpsO RNA, demonstrating for the first time a particular in vivo processing event that could be catalyzed by both enzymes. Decay intermediates were detected in the pnpA strain only for a lac-rpsO RNA that was untranslated. Analysis of processing of an untranslated lac-rpsO RNA in the pnpA strain shortly after induction of transcription suggested that endonuclease cleavage at 3'-proximal sites was an early step in turnover of mRNA.
Figures
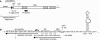




References
-
- Bechhofer, D. H. 2009. Messenger RNA decay and maturation in Bacillus subtilis. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 85231-273. - PubMed
-
- Betz, J. L., H. M. Sasmor, F. Buck, M. Y. Insley, and M. H. Caruthers. 1986. Base substitution mutants of the lac operator: in vivo and in vitro affinities for lac repressor. Gene 50123-132. - PubMed
-
- Britton, R. A., T. Wen, L. Schaefer, O. Pellegrini, W. C. Uicker, N. Mathy, C. Tobin, R. Daou, J. Szyk, and C. Condon. 2007. Maturation of the 5′ end of Bacillus subtilis 16S rRNA by the essential ribonuclease YkqC/RNase J1. Mol. Microbiol. 63127-138. - PubMed
-
- Brosius, J. 1992. Compilation of superlinker vectors. Methods Enzymol. 216469-483. - PubMed
-
- Caruthers, J. M., Y. Feng, D. B. McKay, and S. N. Cohen. 2006. Retention of core catalytic functions by a conserved minimal ribonuclease E peptide that lacks the domain required for tetramer formation. J. Biol. Chem. 28127046-27051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

