Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 19633196
- PMCID: PMC2715325
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901402106
Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease
Abstract
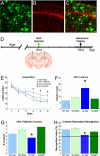
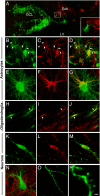
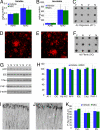
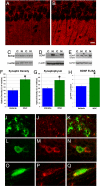
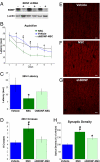
Neural stem cell (NSC) transplantation represents an unexplored approach for treating neurodegenerative disorders associated with cognitive decline such as Alzheimer disease (AD). Here, we used aged triple transgenic mice (3xTg-AD) that express pathogenic forms of amyloid precursor protein, presenilin, and tau to investigate the effect of neural stem cell transplantation on AD-related neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction. Interestingly, despite widespread and established Ass plaque and neurofibrillary tangle pathology, hippocampal neural stem cell transplantation rescues the spatial learning and memory deficits in aged 3xTg-AD mice. Remarkably, cognitive function is improved without altering Ass or tau pathology. Instead, the mechanism underlying the improved cognition involves a robust enhancement of hippocampal synaptic density, mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Gain-of-function studies show that recombinant BDNF mimics the beneficial effects of NSC transplantation. Furthermore, loss-of-function studies show that depletion of NSC-derived BDNF fails to improve cognition or restore hippocampal synaptic density. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that neural stem cells can ameliorate complex behavioral deficits associated with widespread Alzheimer disease pathology via BDNF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ebert AD, Beres AJ, Barber AE, Svendsen CN. Human neural progenitor cells over-expressing IGF-1 protect dopamine neurons and restore function in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2008;209:213–223. - PubMed
-
- Lu P, Jones LL, Snyder EY, Tuszynski MH. Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2003;181(2):115–129. - PubMed
-
- Park KI, et al. Neural stem cells may be uniquely suited for combined gene therapy and cell replacement: Evidence from engraftment of Neurotrophin-3-expressing stem cells in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2006;199(1):179–190. - PubMed
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, LaFerla FM. Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron. 2005;45(5):675–688. - PubMed
-
- Oddo S, et al. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: Intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron. 2003;39(3):409–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

