A new synthetic compound, 2-OH, enhances interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 19633608
- PMCID: PMC6255383
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules14072345
A new synthetic compound, 2-OH, enhances interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
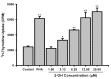
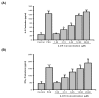
A new synthetic compound, 6-hydroxy-2-tosylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one (2-OH), was selected for immunopharmacological activity tests. The effects of 2-OH on human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) proliferation were determined by tritiated thymidine uptake. Compared to phytohemagglutinin (PHA; 5 microg/mL) stimulation, 2-OH significantly enhanced PBMC proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. The 50% enhancement activity (EC(50)) for 2-OH was 4.4+/-0.1 microM. In addition, effects of 2-OH on interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production in PBMC were determined by enzyme immunoassay. Results demonstrated that 2-OH stimulated IL-2 and IFN-gamma production in PBMC. Data from reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR indicated that IL-2 and IFN-gamma mRNA expression in PBMC could be induced by 2-OH. Therefore, 2-OH enhanced IL-2 and IFN-gamma production in PBMC by modulation their gene expression. We suggest that 2-OH may be an immunomodulatory agent.
Figures


References
-
- Numata A., Ibuka I. Alkaloids from ants and other insects. In: Brossi A., editor. The Alkaloids. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 1987. p. 193.
-
- San Miguel J.F., Schlag R., Khuageva N.K., Dimopoulos M.A., Shpilberg O., Kropff M., Spicka I., Petrucci M.T., Palumbo A., Samoilova O.S., Dmoszynska A., Abdulkadyrov K.M., Schots R., Jiang B., Mateos M.V., Anderson K.C., Esseltine D.L., Liu K., Cakana A., van de Velde H., Richardson P.G. VISTA Trial Investigators. Bortezomib plus melphalan and prednisone for initial treatment of multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;359:906–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

