Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
- PMID: 19633656
- PMCID: PMC3115752
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2002
Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
Abstract
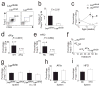
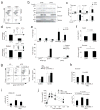
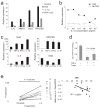
Obesity is accompanied by chronic, low-grade inflammation of adipose tissue, which promotes insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes. These findings raise the question of how fat inflammation can escape the powerful armamentarium of cells and molecules normally responsible for guarding against a runaway immune response. CD4(+) Foxp3(+) T regulatory (T(reg)) cells with a unique phenotype were highly enriched in the abdominal fat of normal mice, but their numbers were strikingly and specifically reduced at this site in insulin-resistant models of obesity. Loss-of-function and gain-of-function experiments revealed that these T(reg) cells influenced the inflammatory state of adipose tissue and, thus, insulin resistance. Cytokines differentially synthesized by fat-resident regulatory and conventional T cells directly affected the synthesis of inflammatory mediators and glucose uptake by cultured adipocytes. These observations suggest that harnessing the anti-inflammatory properties of T(reg) cells to inhibit elements of the metabolic syndrome may have therapeutic potential.
Figures



Comment in
-
T-ing up inflammation in fat.Nat Med. 2009 Aug;15(8):846-7. doi: 10.1038/nm0809-846. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19661987 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Bosello O, Zamboni M. Visceral obesity and metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev. 2000;1:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:911–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

