A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes
- PMID: 19633714
- PMCID: PMC2711349
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006372
A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2009;4(12). doi: 10.1371/annotation/50c43133-0df5-4b8b-8975-8cc37d4f2f26 doi: 10.1371/annotation/50c43133-0df5-4b8b-8975-8cc37d4f2f26
Abstract
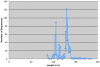
Background: Massively parallel pyrosequencing of amplicons from the V6 hypervariable regions of small-subunit (SSU) ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes is commonly used to assess diversity and richness in bacterial and archaeal populations. Recent advances in pyrosequencing technology provide read lengths of up to 240 nucleotides. Amplicon pyrosequencing can now be applied to longer variable regions of the SSU rRNA gene including the V9 region in eukaryotes.
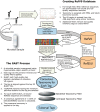
Methodology/principal findings: We present a protocol for the amplicon pyrosequencing of V9 regions for eukaryotic environmental samples for biodiversity inventories and species richness estimation. The International Census of Marine Microbes (ICoMM) and the Microbial Inventory Research Across Diverse Aquatic Long Term Ecological Research Sites (MIRADA-LTERs) projects are already employing this protocol for tag sequencing of eukaryotic samples in a wide diversity of both marine and freshwater environments.
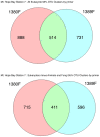
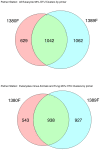
Conclusions/significance: Massively parallel pyrosequencing of eukaryotic V9 hypervariable regions of SSU rRNA genes provides a means of estimating species richness from deeply-sampled populations and for discovering novel species from the environment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Amaral-Zettler L, Peplies J, Ramette A, Fuchs B, Ludwig W, et al. Proceedings of the international workshop on Ribosomal RNA technology, April 7–9, 2008, Bremen, Germany. Syst and Appl Microbiol. 2008;31:258–268. - PubMed
-
- Olsen GJ, Lane DJ, Giovannoni SJ, Pace NR. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. - PubMed
-
- Pace NR, Stahl DA, Lane DJ, Olsen GJ. Analyzing natural microbial populations by rRNA sequences. ASM News. 1985;51:4–12.
-
- Kysela DT, Palacios C, Sogin ML. Serial Analysis of V6-ribosomal sequence tags (SARST-V6): A method for efficient, high-throughput analysis of microbial community composition. Environ Microbiol. 2005;7:356–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

