Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression
- PMID: 19633716
- PMCID: PMC2712071
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006377
Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression
Abstract
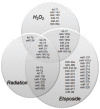
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, highly conserved, non-coding RNA that alter protein expression and regulate multiple intracellular processes, including those involved in the response to cellular stress. Alterations in miRNA expression may occur following exposure to several stress-inducing anticancer agents including ionizing radiation, etoposide, and hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)).
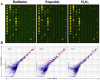
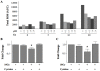
Methodology/principal findings: Normal human fibroblasts were exposed to radiation, H(2)O(2), or etoposide at doses determined by clonogenic cell survival curves. Total RNA was extracted and miRNA expression was determined by microarray. Time course and radiation dose responses were determined using RT-PCR for individual miRNA species. Changes in miRNA expression were observed for 17 miRNA species following exposure to radiation, 23 after H(2)O(2) treatment, and 45 after etoposide treatment. Substantial overlap between the miRNA expression changes between agents was observed suggesting a signature miRNA response to cell stress. Changes in the expression of selected miRNA species varied in response to radiation dose and time. Finally, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) increased with increasing doses of radiation and pre-treatment with the thiol antioxidant cysteine decreased both ROS production and the miRNA response to radiation.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate a common miRNA expression signature in response to exogenous genotoxic agents including radiation, H(2)O(2), and etoposide. Additionally, pre-treatment with cysteine prevented radiation-induced alterations in miRNA expression which suggests that miRNAs are responsive to oxidative stress. Taken together, these results imply that miRNAs play a role in cellular defense against exogenous stress and are involved in the generalized cellular response to genotoxic oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
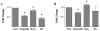
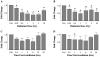
Similar articles
-
Involvement of miRNAs in cellular responses to radiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2022;98(3):479-488. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2028923. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Int J Radiat Biol. 2022. PMID: 35030053
-
Ionizing radiation-induced microRNA expression changes in cultured RGC-5 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4173-4178. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3938. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26081562 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR analysis of micro-RNA expression in ionizing radiation-treated cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009 Feb;24(1):49-56. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2008.0513. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009. PMID: 19216629
-
The role of miRNA in the direct and indirect effects of ionizing radiation.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011 Nov;50(4):491-9. doi: 10.1007/s00411-011-0386-5. Epub 2011 Sep 18. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21928045 Review.
-
miRNAs, oxidative stress, and cancer: A comprehensive and updated review.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov;235(11):8812-8825. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29724. Epub 2020 May 11. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32394436 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic and differential regulation in the microRNA expression in the developing and mature cataractous rat lens.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Sep;17(9):1146-59. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12094. Epub 2013 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23844765 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the ionizing radiation response and in radiotherapy.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Feb;23(1):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23453900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhamnetin and cirsiliol induce radiosensitization and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by miR-34a-mediated suppression of Notch-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 20;288(38):27343-27357. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.490482. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23902763 Free PMC article.
-
Differential oxidative stress gene expression profile in mouse brain after proton exposure.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010 Sep;46(8):718-25. doi: 10.1007/s11626-010-9330-2. Epub 2010 Jul 7. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010. PMID: 20607620
-
microRNAome changes in bystander three-dimensional human tissue models suggest priming of apoptotic pathways.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Oct;31(10):1882-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq119. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20643754 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

