The languages of medicine
- PMID: 19633751
- PMCID: PMC2696676
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2008.0037
The languages of medicine
Figures


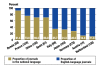
References
-
- Lippert H. Rückzug der deutschen Sprache aus der Medizin? Med Klin. 1978;73:487–496. - PubMed
-
- Navarro FA. Englisch oder Deutsch? Die Sprache der Medizin aufgrund der in der Deutschen Medizinischen Wochenschrift erschienenen Literaturangaben (1920-1995) Dtsch Med Wschr. 1996;121:1561–1566. - PubMed
-
- Navarro FA. Die Sprache der Medizin in der Schweiz von 1920 bis 1995. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1997;127:1565–1573. - PubMed
-
- Navarro FA. Die Sprache der Medizin in Österreich (1920-1925) Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1996;108:362–369. - PubMed
-
- Navarro FA. L’importance de l’anglais et du francais sur la base des references bibliographiques de travaux originaux publies dans La Presse Medicale. La Presse Medicale. 1995;24:1547–1551.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

