Universal intervention effects on substance use among young adults mediated by delayed adolescent substance initiation
- PMID: 19634956
- PMCID: PMC2876977
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016029
Universal intervention effects on substance use among young adults mediated by delayed adolescent substance initiation
Abstract
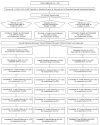
In this article, the authors examine whether delayed substance initiation during adolescence, achieved through universal family-focused interventions conducted in middle school, can reduce problematic substance use during young adulthood. Sixth-grade students enrolled in 33 rural midwestern schools and their families were randomly assigned to 3 experimental conditions. Self-report questionnaires provided data at 7 time points for the Iowa Strengthening Families Program (ISFP), Preparing for the Drug Free Years (PDFY), and control groups through young adulthood. Five young adult substance frequency measures (drunkenness, alcohol-related problems, cigarettes, illicit drugs, and polysubstance use) were modeled as distal outcomes affected by the average level and rate of increase in substance initiation across the adolescent years in latent growth curve analyses. Results show that the models fit the data and that they were robust across outcomes and interventions, with more robust effects found for ISFP. The addition of direct intervention effects on young adult outcomes was not supported, suggesting long-term effects were primarily indirect. Relative reduction rates were calculated to quantify intervention-control differences on the estimated proportion of young adults indicating problematic substance use; they ranged from 19% to 31% for ISFP and from 9% to 16% for PDFY.
Figures

Comment in
-
Family-Based Interventions in Preventing Children and Adolescents from Using Tobacco: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Acad Pediatr. 2016 Jul;16(5):419-429. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2015.12.006. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Acad Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26892909 Review.
References
-
- Ackerman S, Zuroff DC, Moskowitz DS. Generativity in midlife and young adults: Links to agency, communion, and subjective well-being. International Journal of Aging and Human Development. 2000;50:17–41. - PubMed
-
- Akers RL. Deviant behavior: A social learning approach. 2nd. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Press; 1977.
-
- Alexander JF, Robbins MS, Sexton TL. Family-based interventions with older, at-risk youth: From promise to proof to practice. The Journal of Primary Prevention. 2000;21:185–205.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th. Washington, DC: Author; 2000. text rev.
-
- Anthony J. Selected issued pertinent to epidemiology of adolescent drug use and dependence. Invited presentation at the annual meeting of the Annenberg Commission on Adolescent Substance Abuse; Philadelphia. 2003. Aug 1,

