Jasmonate-dependent plant defense restricts thrips performance and preference
- PMID: 19635132
- PMCID: PMC2724403
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-97
Jasmonate-dependent plant defense restricts thrips performance and preference
Abstract
Background: The western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis [Pergande]) is one of the most important insect herbivores of cultivated plants. However, no pesticide provides complete control of this species, and insecticide resistance has emerged around the world. We previously reported the important role of jasmonate (JA) in the plant's immediate response to thrips feeding by using an Arabidopsis leaf disc system. In this study, as the first step toward practical use of JA in thrips control, we analyzed the effect of JA-regulated Arabidopsis defense at the whole plant level on thrips behavior and life cycle at the population level over an extended period. We also studied the effectiveness of JA-regulated plant defense on thrips damage in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis).
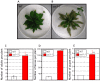
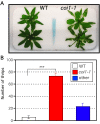
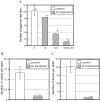
Results: Thrips oviposited more on Arabidopsis JA-insensitive coi1-1 mutants than on WT plants, and the population density of the following thrips generation increased on coi1-1 mutants. Moreover, thrips preferred coi1-1 mutants more than WT plants. Application of JA to WT plants before thrips attack decreased the thrips population. To analyze these important functions of JA in a brassica crop plant, we analyzed the expression of marker genes for JA response in B. rapa. Thrips feeding induced expression of these marker genes and significantly increased the JA content in B. rapa. Application of JA to B. rapa enhanced plant resistance to thrips, restricted oviposition, and reduced the population density of the following generation.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the JA-regulated plant defense restricts thrips performance and preference, and plays an important role in the resistance of Arabidopsis and B. rapa to thrips damage.
Figures





References
-
- Kessler A, Baldwin IT. Plant responses to insect herbivory: the emerging molecular analysis. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2002;53:299–328. - PubMed
-
- Howe GA, Jander G. Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2008;59:41–66. - PubMed
-
- Howe GA, Schaller A. Direct defenses in plants and their induction by wounding and insect herbivores. In: Schaller A, editor. Induced Plant Resistance to Herbivory. New York, Springer; 2008. pp. 7–29.
-
- Van Poecke RMP. The Arabidopsis Book. Rockville, MD: American Society of Plant Biologists; 2008. Arabidopsis-insect interactions.http://www.aspb.org/publications/arabidopsis/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kahl J, Siemens DH, Aerts RJ, Gabler R, Kuhnemann F, Preston CA, Baldwin IT. Herbivore-induced ethylene suppresses a direct defense but not a putative indirect defense against an adapted herbivore. Planta. 2000;210:336–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

