Kinetic cell-based morphological screening: prediction of mechanism of compound action and off-target effects
- PMID: 19635408
- PMCID: PMC2836189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.05.011
Kinetic cell-based morphological screening: prediction of mechanism of compound action and off-target effects
Abstract
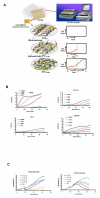
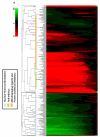
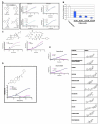
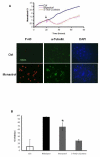
We describe a cell-based kinetic profiling approach using impedance readout for monitoring the effect of small molecule compounds. This noninvasive readout allows continuous sampling of cellular responses to biologically active compounds and the ensuing kinetic profile provides information regarding the temporal interaction of compounds with cells. The utility of this approach was tested by screening a library containing FDA approved drugs, experimental compounds, and nature compounds. Compounds with similar activity produced similar impedance-based time-dependent cell response profiles (TCRPs). The compounds were clustered based on TCRP similarity. We identified novel mechanisms for existing drugs, confirmed previously reported calcium modulating activity for COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib, and identified an additional mechanism for the experimental compound monastrol. We also identified and characterized a new antimitotic agent. Our findings indicate that the TCRP approach provides predictive mechanistic information for small molecule compounds.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham RT. Signalomic signatures enlighten drug profiling. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:295–296. - PubMed
-
- Abraham VC, Towne DL, Waring JF, Warrior U, Burns DJ. Application of a high-content multiparameter cytotoxicity assay to prioritize compounds based on toxicity potential in humans. J Biomol Screen. 2008;13:527–537. - PubMed
-
- Addeo R, Casale F, Caraglia M, D’Angelo V, Crisci S, Abbruzzese A, Di Tullio MT, Indolfi P. Glucocorticoids induce G1 arrest of lymphoblastic cells through retinoblastoma protein Rb1 dephosphorylation in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004;3:470–476. - PubMed
-
- Aizu-Yokota E, Ichinoseki K, Sato Y. Microtubule disruption induced by estradiol in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative human breast cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1994;15:1875–1879. - PubMed
-
- Atienza JM, Yu N, Kirstein SL, Xi B, Wang X, Xu X, Abassi YA. Dynamic and label-free cell-based assays using the real-time cell electronic sensing system. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2006;4:597–607. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

