Targeted manipulation of mammalian genomes using designed zinc finger nucleases
- PMID: 19635463
- PMCID: PMC2744961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.112
Targeted manipulation of mammalian genomes using designed zinc finger nucleases
Abstract
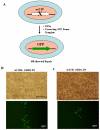
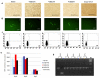
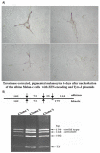
Targeted introduction of a double-stranded break (DSB) using designer zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) in mammalian cells greatly enhances gene targeting - homologous recombination (HR) at a chosen endogenous target gene, which otherwise is limited by low spontaneous rate of HR. Here, we report that efficient ZFN-mediated gene correction occurs at a transduced, transcriptionally active, mutant GFP locus by homology-directed repair, and that efficient mutagenesis by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) occurs at the endogenous, transcriptionally silent, CCR5 locus in HEK293 Flp-In cells, using designed 3- and 4-finger ZFNs. No mutagenesis by NHEJ was observed at the CCR2 locus, which has ZFN sites that are distantly related to the targeted CCR5 sites. We also observed efficient ZFN-mediated correction of a point mutation at the endogenous mutant tyrosinase chromosomal locus in albino mouse melanocytes, using designed 3-finger ZFNs. Furthermore, re-engineered obligate heterodimer FokI nuclease domain variants appear to completely eliminate or greatly reduce the toxicity of ZFNs to mammalian cells, including human cells.
Figures
References
-
- Capecchi MR. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989;244:1288–1292. - PubMed
-
- Jasin M. Genetic manipulation of genomes with rare-cutting endonucleases. Trends Genet. 1996;12:224–228. - PubMed
-
- Mani M, Kandavelou K, Dy JF, Durai S, Chandrasegaran S. Design, engineering and characterization of zinc finger nucleases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;335:447–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

