c-Cbl tyrosine kinase-binding domain mutant G306E abolishes the interaction of c-Cbl with CD38 and fails to promote retinoic acid-induced cell differentiation and G0 arrest
- PMID: 19635790
- PMCID: PMC2757968
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014241
c-Cbl tyrosine kinase-binding domain mutant G306E abolishes the interaction of c-Cbl with CD38 and fails to promote retinoic acid-induced cell differentiation and G0 arrest
Abstract
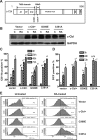
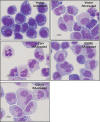
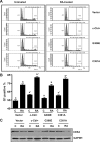
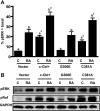
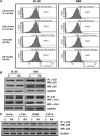
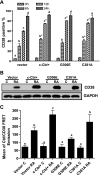
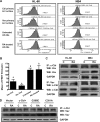
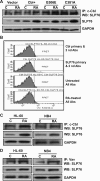
Retinoic acid (RA) causes HL-60 human myeloblastic leukemia cell myeloid differentiation that is dependent on MAPK signaling. The process is propelled by c-Cbl, which binds the CD38 receptor as part of a signaling complex generating MAPK signaling. Here we report that the capability of c-Cbl to do this is lost in the G306E tyrosine kinase-binding domain mutant. Unlike wild-type (WT) c-Cbl, the G306E mutant c-Cbl fails to propel RA-induced differentiation, and disrupts the normal association with CD38. The G306E mutant does, like WT c-Cbl, co-immunoprecipitate with Vav, Slp-76, and p38. But unlike WT c-Cbl, does not cause MAPK signaling. In contrast, the C381A Ring finger domain mutant functions like WT c-Cbl. It binds CD38 and is part of the same apparent c-Cbl/Slp-76/Vav/p38 signaling complex. The C381A mutant causes MAPK signaling and propels RA-induced differentiation. In addition to HL-60 cells and their WT or mutant c-Cbl stable transfectants, the c-Cbl/Vav/Slp-76 complex is also found in NB4 cells where c-Cbl was previously also found to bind CD38. The data are consistent with a model in which the G306E mutant c-Cbl forms a signaling complex that includes Slp-76, Vav, and p38; but does not drive MAPK signaling because it fails to bind the CD38 receptor. Without the G306E mutation the c-Cbl unites CD38 with the signaling complex and delivers a MAPK signal that drives RA-induced differentiation. The results demonstrate the importance of the Gly306 residue in the ability of c-Cbl to propel RA-induced differentiation.
Figures
References
-
- Yen A., Roberson M. S., Varvayanis S., Lee A. T. (1998) Cancer Res. 58, 3163–3172 - PubMed
-
- Yen A., Roberson M. S., Varvayanis S. (1999) In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 35, 527–532 - PubMed
-
- Mann G., Reinhardt D., Ritter J., Hermann J., Schmitt K., Gadner H., Creutzig U. (2001) Ann. Hematol. 80, 417–422 - PubMed
-
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. (1977) Nature 270, 347–349 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

