Galectin-1 co-clusters CD43/CD45 on dendritic cells and induces cell activation and migration through Syk and protein kinase C signaling
- PMID: 19635795
- PMCID: PMC2785374
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.037507
Galectin-1 co-clusters CD43/CD45 on dendritic cells and induces cell activation and migration through Syk and protein kinase C signaling
Abstract
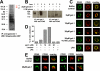
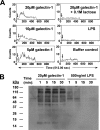
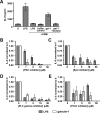
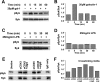
Galectin-1 is a galactoside-binding lectin expressed in multiple tissues that has pleiotropic immunomodulatory functions. We previously showed that galectin-1 activates human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDCs) and triggers a specific genetic program that up-regulates DC migration through the extracellular matrix, an integral property of mucosal DCs. Here, we identify the galectin-1 receptors on MDDCs and immediate downstream effectors of galectin-1-induced MDDC activation and migration. Galectin-1 binding to surface CD43 and CD45 on MDDCs induced an unusual unipolar co-clustering of these receptors and activates a dose-dependent calcium flux that is abrogated by lactose. Using a kinome screen and a systems biology approach, we identified Syk and protein kinase C tyrosine kinases as mediators of the DC activation effects of galectin-1. Galectin-1, but not lipopolysaccharide, stimulated Syk phosphorylation and recruitment of phosphorylated Syk to the CD43 and CD45 co-cluster on MDDCs. Inhibitors of Syk and protein kinase C signaling abrogated galectin-1-induced DC activation as monitored by interleukin-6 production; and MMP-1, -10, and -12 gene up-regulation; and enhanced migration through the extracellular matrix. The latter two are specific features of galectin-1-activated DCs. Interestingly, we also found that galectin-1 can prime DCs to respond more quickly to low dose lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Finally, we underscore the biological relevance of galectin-1-enhanced DC migration by showing that intradermal injection of galectin-1 in MRL-fas mice, which have a defect in skin DC emigration, increased the in vivo migration of dermal DCs to draining lymph nodes.
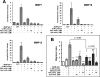
Figures



References
-
- Banchereau J., Briere F., Caux C., Davoust J., Lebecque S., Liu Y. J., Pulendran B., Palucka K. (2000) Annu Rev. Immunol. 18, 767–811 - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J., Steinman R. M. (1998) Nature 392, 245–252 - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Takeda K. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 499–511 - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki A., Medzhitov R. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5, 987–995 - PubMed
-
- Gallucci S., Matzinger P. (2001) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 114–119 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI060694/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI060694/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM08042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI080778/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007126/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016042/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI07126-30/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL096392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080778/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL096392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR056465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

