TAF4/4b x TAF12 displays a unique mode of DNA binding and is required for core promoter function of a subset of genes
- PMID: 19635797
- PMCID: PMC2785316
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.011486
TAF4/4b x TAF12 displays a unique mode of DNA binding and is required for core promoter function of a subset of genes
Abstract
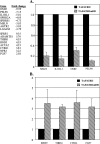
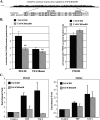
The major core promoter-binding factor in polymerase II transcription machinery is TFIID, a complex consisting of TBP, the TATA box-binding protein, and 13 to 14 TBP-associated factors (TAFs). Previously we found that the histone H2A-like TAF paralogs TAF4 and TAF4b possess DNA-binding activity. Whether TAF4/TAF4b DNA binding directs TFIID to a specific core promoter element or facilitates TFIID binding to established core promoter elements is not known. Here we analyzed the mode of TAF4b.TAF12 DNA binding and show that this complex binds DNA with high affinity. The DNA length required for optimal binding is approximately 70 bp. Although the complex displays a weak sequence preference, the nucleotide composition is less important than the length of the DNA for high affinity binding. Comparative expression profiling of wild-type and a DNA-binding mutant of TAF4 revealed common core promoter features in the down-regulated genes that include a TATA-box and an Initiator. Further examination of the PEL98 gene from this group showed diminished Initiator activity and TFIID occupancy in TAF4 DNA-binding mutant cells. These findings suggest that DNA binding by TAF4/4b-TAF12 facilitates the association of TFIID with the core promoter of a subset of genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TAF4 nucleates a core subcomplex of TFIID and mediates activated transcription from a TATA-less promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605499103. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16895980 Free PMC article.
-
A transcription factor IIA-binding site differentially regulates RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription in a promoter context-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11873-11885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770412. Epub 2017 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28539359 Free PMC article.
-
TAF4, a subunit of transcription factor II D, directs promoter occupancy of nuclear receptor HNF4A during post-natal hepatocyte differentiation.Elife. 2014 Sep 10;3:e03613. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03613. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25209997 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental regulation of transcription initiation: more than just changing the actors.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Oct;20(5):533-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.06.004. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010. PMID: 20598874 Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding the structure and function of general transcription factor TFIID.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jul;66(13):2123-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0009-3. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19308322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated analysis of recurrent properties of cancer genes to identify novel drivers.Genome Biol. 2013 May 29;14(5):R52. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-5-r52. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718799 Free PMC article.
-
αα-Hub domains and intrinsically disordered proteins: A decisive combo.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100226. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.012928. Epub 2020 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33361159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The elongation factor Spt5 facilitates transcription initiation for rapid induction of inflammatory-response genes.Nat Commun. 2016 May 16;7:11547. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11547. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27180651 Free PMC article.
-
TAF-4 is required for the life extension of isp-1, clk-1 and tpk-1 Mit mutants.Aging (Albany NY). 2013 Oct;5(10):741-58. doi: 10.18632/aging.100604. Aging (Albany NY). 2013. PMID: 24107417 Free PMC article.
-
De novo putative loss-of-function variants in TAF4 are associated with a neuro-developmental disorder.Hum Mutat. 2022 Dec;43(12):1844-1851. doi: 10.1002/humu.24444. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 35904126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juven-Gershon T., Hsu J. Y., Kadonaga J. T. (2006) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34, 1047–1050 - PubMed
-
- Smale S. T. (2001) Genes Dev. 15, 2503–2508 - PubMed
-
- Smale S. T., Kadonaga J. T. (2003) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 449–479 - PubMed
-
- Matangkasombut O., Auty R., Buratowski S. (2004) Adv. Protein Chem. 67, 67–92 - PubMed
-
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. (1985) Cell 43, 165–175 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

