Artemisone and artemiside control acute and reactivated toxoplasmosis in a murine model
- PMID: 19635951
- PMCID: PMC2764205
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00502-09
Artemisone and artemiside control acute and reactivated toxoplasmosis in a murine model
Abstract
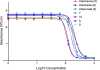
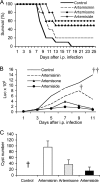
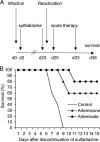
Immunocompromised patients are at risk of developing toxoplasmosis, and although chemotherapy is available, standard treatments are often complicated by severe side effects. Artemisinin is a new highly potent antimalarial drug that has activity against Toxoplasma gondii in vitro. However, artemisinin derivatives have previously been ineffective in vivo using a rat model of toxoplasmosis. In the present study, the efficacy of several new artemisinin derivates was investigated for treatment of mice infected with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Artemiside and artemisone displayed better inhibition than either artemisinin or artesunate against the parasite in vitro. Artemiside and artemisone treatment controlled parasite replication in vivo, and mice survived the acute infection. In a murine model of reactivated toxoplasmosis, both drugs increased survival, although artemiside was more effective. These results indicate that these newer derivatives of artemisinin may have potential for treatment of toxoplasmosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteomic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii ME49 derived strains resistant to the artemisinin derivatives artemiside and artemisone implies potential mode of action independent of ROS formation.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2023 Apr;21:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2022.11.005. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36512904 Free PMC article.
-
Single and combination treatment of Toxoplasma gondii infections with a bumped kinase inhibitor and artemisone in vitro and with artemiside in experimentally infected mice.Exp Parasitol. 2023 Dec;255:108655. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2023.108655. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Exp Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37981259 Free PMC article.
-
Absorption of the novel artemisinin derivatives artemisone and artemiside: potential application of Pheroid™ technology.Int J Pharm. 2011 Jul 29;414(1-2):260-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 7. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21596127
-
Malaria and artemisinin derivatives: an updated review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Nov;13(13):1879-902. doi: 10.2174/13895575113136660097. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24070206 Review.
-
Novel use for old drugs: The emerging role of artemisinin and its derivatives in fibrosis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jul;157:104829. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104829. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32360483 Review.
Cited by
-
Subchronic toxicological study of two artemisinin derivatives in dogs.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 16;9(4):e94034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094034. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24739881 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of resistance in vitro reveals mechanisms of artemisinin activity in Toxoplasma gondii.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 26;116(52):26881-26891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914732116. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31806760 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis in mice identifies cysteamine as a novel partner for artemisinin in the treatment of malaria.Mamm Genome. 2011 Aug;22(7-8):486-94. doi: 10.1007/s00335-011-9316-8. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Mamm Genome. 2011. PMID: 21437649 Review.
-
Artemisinin derivatives induce oxidative stress leading to DNA damage and caspase-mediated apoptosis in Theileria annulata-transformed cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Apr 17;21(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01067-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37069625 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated expression of Tim-3 involved in the process of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mouse model.Parasitol Res. 2013 Jul;112(7):2511-21. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3416-1. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23595213
References
-
- Ajzenberg, D., N. Cogné, L. Paris, M. H. Bessieres, P. Thulliez, D. Fillisetti, H. Pelloux, P. Marty, and M. L. Dardé. 2002. Genotype of 86 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis and correlation with clinical findings. J. Infect. Dis. 186:684-689. - PubMed
-
- Ashley, E. A., and N. J. White. 2005. Artemisinin-based combinations. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 18:531-536. - PubMed
-
- Baatz, H., A. Mirashahi, J. Puchta, H. Gumbel, and L. O. Hattenbach. 2006. Reactivation of toxoplasma retinochoroiditis under atovaquone therapy in an immunocompetent patient. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 14:185-187. - PubMed
-
- Barragan, A., and L. D. Sibley. 2003. Migration of Toxoplasma gondii across biological barriers. Trends Microbiol. 11:426-430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

