Oritavancin population pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects and patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections or bacteremia
- PMID: 19635952
- PMCID: PMC2764228
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00231-09
Oritavancin population pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects and patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections or bacteremia
Abstract
Oritavancin is a novel glycopeptide antimicrobial agent with potent in vitro activity against a wide variety of gram-positive bacteria, including multidrug-resistant strains of staphylococci and enterococci. A population pharmacokinetic model was developed to describe the disposition of oritavancin with data from a pooled population of phase 1 healthy subjects and phase 2 and 3 patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections or Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. In addition, the potential influence of factors such as the subject's age, gender, and clinical laboratory measures on oritavancin disposition was evaluated. Oritavancin was administered as both single- and multiple-dose intravenous (i.v.) infusions in fixed doses ranging from 100 to 800 mg or weight-based doses ranging from 0.02 to 10 mg/kg of body weight, with infusion durations ranging from 0.13 to 6.5 h across all studies. The most robust fit to the data (n = 6,290 oritavancin plasma concentrations from 560 subjects) was obtained using a three-compartment model with zero-order i.v. infusion and first-order elimination. The model was parameterized using total clearance (CL), volume of central compartment (Vc), distributional clearances from the central to both the first and second peripheral compartments, and volumes of distribution for both the first and second peripheral compartments. Weight and study phase (phase 1 versus phase 2/3) were identified as significant predictors of the interindividual variability in CL, while body surface area and age were significant for Vc. These results suggest that dose modification may be warranted in patients weighing >110 kg. However, the mild nature of the observed relationships for Vc suggest that dosing adjustments are not necessary for elderly patients.
Figures
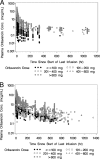
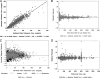
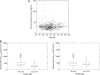
References
-
- Allen, N. E., and T. I. Nicas. 2003. Mechanism of action of oritavancin and related glycopeptide antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 26:511-532. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, R. J. 2006. S-ADAPT/MCPEM user's guide: software for pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and population data analysis. http://bmsr.usc.edu/software/ADAPT/SADAPTsoftware.html.
-
- Bhavnani, S. M., J. S. Owen, J. S. Loutit, S. B. Porter, and P. G. Ambrose. 2004. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of ascending single intravenous doses of oritavancin administered to healthy human subjects. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 50:95-102. - PubMed
-
- Bhavnani, S. M., C. M. Rubino, A. Forrest, D. Lehoux, O. O. Okusanya, G. L. Drusano, K. A. Rodvold, W. A. Craig, P. G. Ambrose, and T. R. Parr. 2007. Use of PK-PD principles to guide clinical drug development for oritavancin, abstr. A-51. Abstr. 47th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
-
- Cockcroft, D. W., and M. H. Gault. 1976. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31-41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

