In vitro 24-hour time-kill studies of vancomycin and linezolid in combination versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19635959
- PMCID: PMC2764166
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00237-09
In vitro 24-hour time-kill studies of vancomycin and linezolid in combination versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
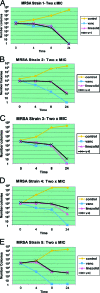
Many clinicians are trying unique strategies, including vancomycin and linezolid in combination, for treatment of patients who do not respond to conventional therapy against methicillin (meticillin)-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. In our study, which illustrated in vitro activity only, no synergistic activity was seen when the two agents were combined. Conversely, antagonistic activity occurred in three of five strains when linezolid was added to vancomycin. Our results indicate that vancomycin and linezolid in combination should be avoided.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance selection studies comparing the activity of razupenem (PTZ601) to vancomycin and linezolid against eight methicillin-resistant and two methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Jul;53(7):3118-21. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00183-09. Epub 2009 May 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19433566 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activities of LTX-109, a synthetic antimicrobial peptide, against methicillin-resistant, vancomycin-intermediate, vancomycin-resistant, daptomycin-nonsusceptible, and linezolid-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Aug;56(8):4478-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00194-12. Epub 2012 May 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22585222 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of in vitro efficacy of linezolid and vancomycin by determining their minimum inhibitory concentrations against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).J Pak Med Assoc. 2011 Apr;61(4):356-9. J Pak Med Assoc. 2011. PMID: 21465972
-
In vitro and in vivo activities of linezolid alone and combined with vancomycin and imipenem against Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Nov;29(11):1361-7. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-1007-y. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20680368 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of linezolid alone and in combination with gentamicin, vancomycin or rifampicin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by time-kill curve methods.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003 Apr;51(4):857-64. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg160. Epub 2003 Mar 13. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12654769
Cited by
-
Efficacy of vancomycin in combination with various antimicrobial agents against clinical methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.Pak J Med Sci. 2021 Jan-Feb;37(1):151-156. doi: 10.12669/pjms.37.1.2887. Pak J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33437268 Free PMC article.
-
Observed Antagonistic Effect of Linezolid on Daptomycin or Vancomycin Activity against Biofilm-Forming Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an In Vitro Pharmacodynamic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Dec;59(12):7790-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01604-15. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26369963 Free PMC article.
-
The use of bone cement for the localized, controlled release of the antibiotics vancomycin, linezolid, or fusidic acid: effect of additives on drug release rates and mechanical strength.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2011 Apr;1(2):121-31. doi: 10.1007/s13346-011-0015-5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 25788111
-
A case of community-acquired Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) necrotizing pneumonia successfully treated with two anti-MRSA drugs.Respir Med Case Rep. 2024 Apr 18;49:102023. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2024.102023. eCollection 2024. Respir Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38681212 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Antibiotic Exposure Selectively Alters the Development of Vancomycin Intermediate Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jan 25;62(2):e02100-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02100-17. Print 2018 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29158272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry, A. L., W. C. Craig, H. Nadler, L. B. Reller, C. C. Sanders, and J. M. Swenson. 1999. Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents; approved guideline. NCCLS document M26-A. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, PA.
-
- Deville, J. G., S. Adler, P. H. Azimi, B. A. Jantausch, M. R. Morfin, S. Beltran, B. Edge-Padbury, S. Naberhuis-Stehouwer, and J. B. Bruss. 2003. Linezolid versus vancomycin in the treatment of known or suspected resistant gram-positive infections in neonates. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 22(Suppl.):S158-S163. - PubMed
-
- Drinka, P. J., M. E. Stemper, C. D. Gauerke, J. E. Miller, B. M. Goodman, and K. D. Reed. 2005. Clustering of multiple endemic strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a nursing home: an 8-year study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 26:215-218. - PubMed
-
- Jacqueline, C., J. Callion, V. Le Mabecque, A. F. Miegeville, P. Y. Donnio, D. Bugnon, and G. Potel. 2003. In vitro activity of linezolid alone and in combination with gentamicin, vancomycin or rifampicin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by time-kill curve methods. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51:857-864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical