In vitro 24-hour time-kill studies of vancomycin and linezolid in combination versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19635959
- PMCID: PMC2764166
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00237-09
In vitro 24-hour time-kill studies of vancomycin and linezolid in combination versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
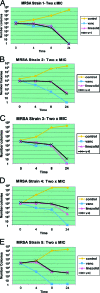
Many clinicians are trying unique strategies, including vancomycin and linezolid in combination, for treatment of patients who do not respond to conventional therapy against methicillin (meticillin)-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. In our study, which illustrated in vitro activity only, no synergistic activity was seen when the two agents were combined. Conversely, antagonistic activity occurred in three of five strains when linezolid was added to vancomycin. Our results indicate that vancomycin and linezolid in combination should be avoided.
Figures
References
-
- Barry, A. L., W. C. Craig, H. Nadler, L. B. Reller, C. C. Sanders, and J. M. Swenson. 1999. Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents; approved guideline. NCCLS document M26-A. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, PA.
-
- Deville, J. G., S. Adler, P. H. Azimi, B. A. Jantausch, M. R. Morfin, S. Beltran, B. Edge-Padbury, S. Naberhuis-Stehouwer, and J. B. Bruss. 2003. Linezolid versus vancomycin in the treatment of known or suspected resistant gram-positive infections in neonates. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 22(Suppl.):S158-S163. - PubMed
-
- Drinka, P. J., M. E. Stemper, C. D. Gauerke, J. E. Miller, B. M. Goodman, and K. D. Reed. 2005. Clustering of multiple endemic strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a nursing home: an 8-year study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 26:215-218. - PubMed
-
- Jacqueline, C., J. Callion, V. Le Mabecque, A. F. Miegeville, P. Y. Donnio, D. Bugnon, and G. Potel. 2003. In vitro activity of linezolid alone and in combination with gentamicin, vancomycin or rifampicin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by time-kill curve methods. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51:857-864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical