Phase I dose escalation, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of naptumomab estafenatox alone in patients with advanced cancer and with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19636016
- PMCID: PMC2734423
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.2515
Phase I dose escalation, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of naptumomab estafenatox alone in patients with advanced cancer and with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
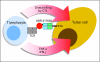
Purpose: Two phase I studies were conducted of ABR-217620 alone or in combination with docetaxel. This is a recombinant fusion protein consisting of a mutated variant of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin E (SEA/E-120) linked to fragment antigen binding moiety of a monoclonal antibody recognizing the tumor-associated antigen 5T4.
Patients and methods: Patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pancreatic cancer (PC), and renal cell cancer (RCC) received 5 daily boluses of ABR-217620 (3-month cycles) in escalating doses to determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD; ABR-217620 dose escalation monotherapy [MONO] study). Doses were selected based on individual patient anti-SEA/E-120 titers pretreatment. Patients with NSCLC received 4 daily, escalating doses of ABR-217620 followed by docetaxel in 21-day cycles (ABR-217620 dose escalation combination with docetaxel [COMBO] study).
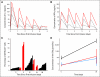
Results: Thirty-nine patients were enrolled in the MONO study and 13 were enrolled in the COMBO study. The monotherapy MTD was 26 microg/kg (NSCLC and PC) and 15 microg/kg (RCC). Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) in the MONO study were fever, hypotension, acute liver toxicity, and vascular leak syndrome. In the COMBO study, the MTD was 22 microg/kg (neutropenic sepsis). Adverse events included grade 1 to 2 fever, hypotension, nausea, and chills. Treatment caused a systemic increase of inflammatory cytokines and selective expansion of SEA/E-120 reactive T-cells. Tumor biopsies demonstrated T-cell infiltration after therapy. Fourteen patients (36%) had stable disease (SD) on day 56 of the MONO study. Two patients (15%) in the COMBO study had partial responses, one in a patient with progressive disease on prior docetaxel, and five patients (38%) had SD on day 56.
Conclusion: ABR-217620 was well tolerated with evidence of immunological activity and antitumor activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Allen TM. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anti-cancer therapy. Nature Reviews/Cancer. 2002;2:750–763. - PubMed
-
- Presta LG. Engineering antibodies for therapy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2002;3:237–256. - PubMed
-
- Kreitman RJ, Wang QC, FitzGerald DJ, et al. Complete regression of human B-cell lymphoma xenografts in mice treated with recombinant anti-CD22 immunotoxin RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 at doses tolerated by cynomolgus monkeys. Int J Cancer. 1999;81:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Kreitman RJ, Squires DR, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 (BL22) in patients with B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6719–6729. - PubMed
-
- Sievers EL, Appelbaum FR, Spielberger RT, et al. Selective ablation of acute myeloid leukemia using antibody-targeted chemotherapy: A phase I study of an anti-CD33 calicheamicin immunoconjugate. Blood. 1999;93:3678–3684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

