The microenvironment in mature B-cell malignancies: a target for new treatment strategies
- PMID: 19636060
- PMCID: PMC4969052
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225326
The microenvironment in mature B-cell malignancies: a target for new treatment strategies
Abstract
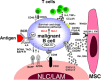
Despite major therapeutic advances, most mature B-cell malignancies remain incurable. Compelling evidence suggests that crosstalk with accessory stromal cells in specialized tissue microenvironments, such as the bone marrow and secondary lymphoid organs, favors disease progression by promoting malignant B-cell growth and drug resistance. Therefore, disrupting the crosstalk between malignant B cells and their milieu is an attractive novel strategy for treating selected mature B-cell malignancies. Here we summarize the current knowledge about the cellular and molecular interactions between neoplastic B lymphocytes and accessory cells that shape a supportive microenvironment, and the potential therapeutic targets that are emerging, together with the new problems they raise. We discuss clinically relevant aspects and provide an outlook into future biologically oriented therapeutic strategies. We anticipate a paradigm shift in the treatment of selected B-cell malignancies, moving from targeting primarily the malignant cells toward combining cytotoxic drugs with agents that interfere with the microenvironment's proactive role. Such approaches hopefully will help eliminating residual disease, thereby improving our current therapeutic efforts.
Figures

References
-
- Albini A, Sporn MB. The tumour microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(2):139–147. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Kipps TJ. Chemokine receptors and stromal cells in the homing and homeostasis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43(3):461–466. - PubMed
-
- Caligaris-Cappio F. Role of the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2003;123(3):380–388. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Peled A. CXCR4 antagonists: targeting the microenvironment in leukemia and other cancers. Leukemia. 2009;23(1):43–52. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Burkle A. The CXCR4 chemokine receptor in acute and chronic leukaemia: a marrow homing receptor and potential therapeutic target. Br J Haematol. 2007;137(4):288–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

