Role of leukemia cell invadosome in extramedullary infiltration
- PMID: 19636064
- PMCID: PMC2756207
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-148643
Role of leukemia cell invadosome in extramedullary infiltration
Abstract
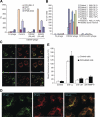
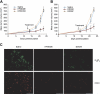
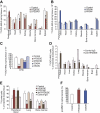
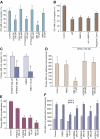
Acute myelogenous leukemias (AMLs) are characterized by medullary and extramedullary invasion. We hypothesized that a supramolecular complex, the leukemia-cell invadosome, which contains certain integrins, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and other as-yet unidentified proteins, is essential for tissue invasion and may be central to the phenotypic diversity observed in the clinic. Here we show that the specific binding of MMP-9 to leukocyte surface beta(2) integrin is required for pericellular proteolysis and migration of AML-derived cells. An efficient antileukemia effect was obtained by the hexapeptide HFDDDE, a motif of the MMP-9 catalytic domain that mediates integrin binding: HFDDDE prevented proMMP-9 binding, transmigration through a human endothelial cell layer, and extracellular matrix degradation. Notably, the functional protein anchorage between beta(2) integrin and proMMP-9 described in this study does not involve the enzymatic active sites targeted by known MMP inhibitors. Taken together, our results provide a biochemical working definition for the human leukemia invadosome. Disruption of specific protein complexes within this supramolecular target complex may yield a new class of anti-AML drugs with anti-invasion (rather than or in addition to cytotoxic) attributes.
Figures

References
-
- Scheinberg D, Maslak P, Weiss M. In: Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. Vita V, Hellman S, Rosenberg S, editors. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 2005. pp. 2404–2432.
-
- Jandl JH. Blood: Textbook of Haematology. 2nd ed. Toronto: Little, Brown and Co; 1996. pp. 1–1200.
-
- Stefanidakis M, Koivunen E. Cell-surface association between matrix metalloproteinases and integrins: role of the complexes in leukocyte migration and cancer progression. Blood. 2006;108(5):1441–1450. - PubMed
-
- Björklund M, Aitio O, Stefanidakis M, et al. Stabilization of the activated aMb2 integrin by a small-molecule inhibits leukocyte migration and recruitment. Biochemistry. 2006;45(9):2862–2871. - PubMed
-
- Suojanen J, Salo T, Sorsa T, Koivunen E. aMb2 integrin modulator exerts antitumor activity in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(6B):3775–3782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

