Esophageal trachealization: a feature of eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 19636182
- PMCID: PMC2841420
- DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.54747
Esophageal trachealization: a feature of eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
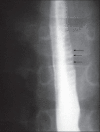
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) is an inflammatory condition characterized by intense eosinophilic infiltration of the esophagus. EE is frequently misdiagnosed as gastroesophageal reflux disease. Here, we present a child with EE and a characteristic endoscopic finding, "ringed esophagus". An 11-year-old Saudi boy presented with dysphagia for 1 year. He had experienced an intermittent sensation of solid food sticking in his chest, which was relieved by drinking liquids. A barium swallow excluded anatomical causes of dysphagia, but revealed multiple-ringed esophagus. Endoscopy showed a furrowing and trachealizing appearance of the entire esophagus. Hisologically, extensive eosinophilic infiltration was a feature in biopsies obtained from the esophagus. The child responded well to a 2-month course of inhaled fluticasone. Symptoms recurred 3 months after discontinuation of therapy, which necessitated resumption of inhaled fluticasone. The endoscopic appearance of multiple esophageal rings should raise suspicion of EE and be confirmed by esophageal biopsies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Walker-Smith JA, Ford RP, Phillips AD. The spectrum of gastrointestinal allergies to food. Ann Allergy. 1984;53:629–36. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults. J Pediatr Gastorenterol Nutr. 2003;37:S23–8. - PubMed
-
- Shiflett DW, Gilliam JH, Wu WC, Austin WE, Ott DJ. Multiple esophageal webs. Gastroenterology. 1979;77:556–9. - PubMed
-
- Munitz HA, Ott DJ, Rocamora LR, Wu WC. Multiple webs of the esophagus. South Med J. 1983;76:405–6. - PubMed
-
- Janisch HD, Eckardt VF. Histological abnormalities in patients with multiple esophageal webs. Dig Dis Sci. 1982;27:503–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
