Immunoreactivity of ICAM-1 in human tumors, metastases and normal tissues
- PMID: 19636402
- PMCID: PMC2713456
Immunoreactivity of ICAM-1 in human tumors, metastases and normal tissues
Abstract
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is implicated to play a role in cancer metastasis, and may serve as a diagnostic tool for tumor prognosis and progression as well as a target for therapeutic intervention. The aim of this study was to carry out a comprehensive survey of ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in normal, malignant and metastatic tissues. We assessed immunoreactivity of ICAM-1 in a total of 300 tissue cores from multiple tissue arrays of normal, malignant, and metastatic tissues by immunohistochemistry. We scored tissue samples for ICAM-1 immunoreactivity on a 0-3 scale, assessed the number of samples exhibiting infiltrating immune cells, and documented ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in some specific cell types. ICAM-1 expression in normal tissues was highest in spleen and absent in the cerebrum, peripheral nerves, pancreas, ovary, breast, uterus, cervix, prostate, lung, larynx, bone marrow, striated muscle, heart, mesothelium, esophagus, small intestine, colon and liver. In primary malignancies, lymphoid tissues received the highest average ICAM-1 score while connective tissue/skin had the lowest average ICAM-1 score. Of the metastatic tissues, those originating from the urinary tract had the highest average ICAM-1 score while those originating from glandular tissues had the lowest average ICAM-1 score. Metastases localized in lymphoid tissues had a higher average ICAM-1 score than those localized in non-lymphoid tissues. Since ICAM-1 is associated with a variety of cancer types and appears to play a role in cancer metastasis, our findings should serve as a helpful resource for investigations of ICAM-1 as a biomarker, as well as a target for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: ICAM-1; immunohistochemistry; metastasis; tissue array; tumor.
Figures
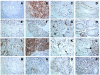
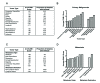
References
-
- Dymicka-Piekarska V, Kemona H. Does colorectal cancer clinical advancement affect adhesion molecules (sP-selectin, sE-selectin and ICAM-1) concentration? Thromb Res. 2009 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Basoglu M, Atamanalp SS, Yildirgan MI, Aydinli B, Ozturk G, Akcay F, Oren D. Correlation between the serum values of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and total sialic acid levels in patients with breast cancer. Eur Surg Res. 2007;39:136–140. - PubMed
-
- Dowlati A, Gray R, Sandler AB, Schiller JH, Johnson DH. Cell adhesion molecules, vascular endothelial growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab–an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1407–1412. - PubMed
-
- Choi Y-L, Xuan YH, Shin YK, Chae SW, Kook MC, Sung RH, Youn SJ, Choi JW, Kim SH. An immunohistochemical study of the expression of adhesion molecules in gallbladder lesions. J Histochem Cytochem. 2004;52:591–601. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
