CD47 regulates collagen I-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and intestinal epithelial cell migration
- PMID: 19636412
- PMCID: PMC2712095
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006371
CD47 regulates collagen I-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and intestinal epithelial cell migration
Abstract
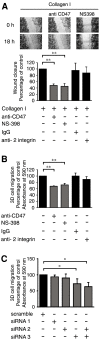
Increased epithelial cell expression of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme is a characteristic event of both inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. We here report the novel findings that collagen I-induced de novo synthesis of COX-2 in intestinal epithelial cells is inhibited by pertussis toxin (PTX) and by an inhibitory peptide selective for the heterotrimeric G alpha(i3)-protein. These findings could be explained by a regulatory involvement of the G-protein-dependent integrin-associated protein CD47. In support of this notion, we observed a collagen I-induced association between CD47 and alpha2 integrins. This association was reduced by a blocking anti-CD47 antibody but not by PTX or a control anti-beta2 antibody. Furthermore, a blocking antibody against CD47, dominant negative CD47 or specific siRNA knock down of CD47, significantly reduced collagen I-induced COX-2 expression. COX-2 has previously been shown to regulate intestinal epithelial cell adhesion and migration. Morphological analysis of intestinal cells adhering to collagen I revealed a co-localisation of CD47 and alpha2 integrins to non-apoptotic membrane blebs enriched in Rho A and F-actin. The blocking CD47 antibody, PTX and a selective COX-2 inhibitor, dramatically inhibited the formation of these blebs. In accordance, migration of these cells on a collagen I-coated surface or through a collagen I gel were significantly reduced by the CD47 blocking antibody, siRNA knock down of CD47 and the COX-2 inhibitor NS-398. In conclusion, we present novel data that identifies the G-protein-dependent CD47 protein as a key regulator of collagen I-induced COX-2 expression and a promoter of intestinal epithelial cell migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ristimaki A. Cyclooxygenase 2: from inflammation to carcinogenesis. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;256 - PubMed
-
- DuBois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, et al. Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J. 1998;12:1063–1073. - PubMed
-
- Williams CS, Shattuck-Brandt RL, DuBois RN. The role of COX-2 in intestinal cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1999;8:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1228–1233. - PubMed
-
- Itzkowitz SH, Yio X. Inflammation and cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: the role of inflammation. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:G7–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

