Studies on Multifunctional Effect of All-Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA) on Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and Its Regulatory Molecules in Human Breast Cancer Cells (MCF-7)
- PMID: 19636436
- PMCID: PMC2712868
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/627840
Studies on Multifunctional Effect of All-Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA) on Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and Its Regulatory Molecules in Human Breast Cancer Cells (MCF-7)
Abstract
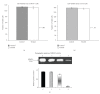
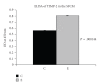
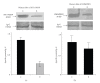
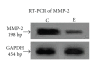
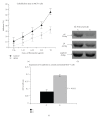
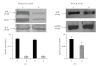
Background. Vitamin A derivative all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is considered as a potent chemotherapeutic drug for its capability of regulating cell growth and differentiation. We studied the effect of ATRA on MMP-2 in MCF-7, human breast cancer cells, and the probable signaling pathways which are affected by ATRA on regulating pro-MMP-2 activity and expression. Methods. Gelatin zymography, RT-PCR, ELISA, Western blot, Immunoprecipitation, and Cell adhesion assay are used. Results. Gelatin zymography showed that ATRA caused a dose-dependent inhibition of pro-MMP-2 activity. ATRA treatment downregulates the expression of MT1-MMP, EMMPRIN, FAK, NF-kB, and p-ERK. However, expression of E-cadherin, RAR, and CRABP increased upon ATRA treatment. Binding of cells to extra cellular matrix (ECM) protein fibronectin reduced significantly after ATRA treatment. Conclusions. The experimental findings clearly showed the inhibition of MMP-2 activity upon ATRA treatment. This inhibitory effect of ATRA on MMP-2 activity in human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) may result due to its inhibitory effect on MT1-MMP, EMMPRIN, and upregulation of TIMP-2. This study is focused on the effect of ATRA on MMP, MMP-integrin-E-cadherin interrelationship, and also the effect of the drug on different signaling molecules which may involve in the progression of malignant tumor development.
Figures


References
-
- Axel DI, Frigge A, Dittmann J, et al. All-trans retinoic acid regulates proliferation, migration, differentiation, and extracellular matrix turnover of human arterial smooth muscle cells. Cardiovascular Research. 2001;49(4):851–862. - PubMed
-
- de Thé H, Chelbi-Alix MK. APL, a model disease for cancer therapies? Oncogene. 2001;20(49):7136–7139. - PubMed
-
- Taraboletti G, Borsotti P, Chirivi RGS, et al. Effect of all trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) on the adhesive and motility properties of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. International Journal of Cancer. 1997;70(1):72–77. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Dokmanovic M, Stein WD, Ardecky RJ, Roninson IB. Agonist and antagonist of retinoic acid receptors cause similar changes in gene expression and induce senescence-like growth arrest in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Research. 2006;66(17):8749–8761. - PubMed
-
- Abu J, Batuwangala M, Herbert K, Symonds P. Retinoic acid and retinoid receptors: potential chemopreventive and therapeutic role in cervical cancer. Lancet Oncology. 2005;6(9):712–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

