Galactosylated LDL nanoparticles: a novel targeting delivery system to deliver antigen to macrophages and enhance antigen specific T cell responses
- PMID: 19637876
- PMCID: PMC2782853
- DOI: 10.1021/mp900081y
Galactosylated LDL nanoparticles: a novel targeting delivery system to deliver antigen to macrophages and enhance antigen specific T cell responses
Abstract
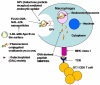
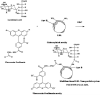
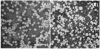
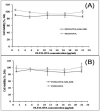
We aim to define the role of Kupffer cells in intrahepatic antigen presentation, using the selective delivery of antigen to Kupffer cells rather than other populations of liver antigen-presenting cells. To achieve this we developed a novel antigen delivery system that can target antigens to macrophages, based on a galactosylated low-density lipoprotein nanoscale platform. Antigen was delivered via the galactose particle receptor (GPr), internalized, degraded and presented to T cells. The conjugation of fluoresceinated ovalbumin (FLUO-OVA) and lactobionic acid with LDL resulted in a substantially increased uptake of FLUO-OVA by murine macrophage-like ANA1 cells in preference to NIH3T3 cells, and by primary peritoneal macrophages in preference to primary hepatic stellate cells. Such preferential uptake led to enhanced proliferation of OVA specific T cells, showing that the galactosylated LDL nanoscale platform is a successful antigen carrier, targeting antigen to macrophages but not to all categories of antigen presenting cells. This system will allow targeted delivery of antigen to macrophages in the liver and elsewhere, addressing the question of the role of Kupffer cells in liver immunology. It may also be an effective way of delivering drugs or vaccines directly at macrophages.
Figures
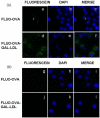
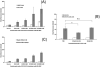
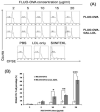
References
-
- Mackay IR. Hepatoimmunology: a perspective. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2002;80(1):36–44. - PubMed
-
- Racanelli V, Rehermann B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology. 2006;43(2 Suppl 1):S54–62. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino P, McCaughan GW, Bowen DG. Role of primary intrahepatic T-cell activation in the ‘liver tolerance effect’. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2002;80(1):84–92. - PubMed
-
- Dong L, Zuo L, Xia S, Gao S, Zhang C, Chen J, Zhang J. Reduction of liver tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression by targeting delivery of antisense oligonucleotides into Kupffer cells protects rats from fulminant hepatitis. J. Gene Med. 2009;11(3):229–239. - PubMed
-
- van Rooijen N. Liposomes for targeting of antigens and drugs: immunoadjuvant activity and liposome-mediated depletion of macrophages. J. Drug Target. 2008;16(7):529–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

