Liver tissue engineering in the evaluation of drug safety
- PMID: 19637986
- PMCID: PMC4110978
- DOI: 10.1517/17425250903160664
Liver tissue engineering in the evaluation of drug safety
Abstract
Assessment of drug-liver interactions is an integral part of predicting the safety profile of new drugs. Existing model systems range from in vitro cell culture models to FDA-mandated animal tests. Data from these models often fail, however, to predict human liver toxicity, resulting in costly failures of clinical trials. In vitro screens based on cultured hepatocytes are now commonly used in early stages of development, but many toxic responses in vivo seem to be mediated by a complex interplay among several different cell types. We discuss some of the evolving trends in liver cell culture systems applied to drug safety assessment and describe an experimental model that captures complex liver physiology through incorporation of heterotypic cell-cell interactions, 3D architecture and perfused flow. We demonstrate how heterotypic interactions in this system can be manipulated to recreate an inflammatory environment and apply the model to test compounds that potentially exhibit idiosyncratic drug toxicity. Finally, we provide a perspective on how the range of existing and emerging in vitro liver culture approaches, from simple to complex, might serve needs across the range of stages in drug discovery and development, including applications in molecular therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Competency of different cell models to predict human hepatotoxic drugs.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014 Nov;10(11):1553-68. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2014.967680. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25297626 Review.
-
In vitro evaluation of potential hepatotoxicity induced by drugs.Curr Pharm Des. 2010 Jun;16(17):1963-77. doi: 10.2174/138161210791208910. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20236064 Review.
-
Evolution of Novel 3D Culture Systems for Studies of Human Liver Function and Assessments of the Hepatotoxicity of Drugs and Drug Candidates.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Oct;121(4):234-238. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12804. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28470941 Review.
-
Characterizing the reproducibility in using a liver microphysiological system for assaying drug toxicity, metabolism, and accumulation.Clin Transl Sci. 2021 May;14(3):1049-1061. doi: 10.1111/cts.12969. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33382907 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of in vitro combination assays of mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis for the estimation of potential risk of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury.J Toxicol Sci. 2016;41(5):605-15. doi: 10.2131/jts.41.605. J Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27665770
Cited by
-
Isolation and co-culture of rat parenchymal and non-parenchymal liver cells to evaluate cellular interactions and response.Sci Rep. 2016 May 4;6:25329. doi: 10.1038/srep25329. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27142224 Free PMC article.
-
Creating tissue on chip constructs in microtitre plates for drug discovery.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 6;8(18):9603-9610. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00849c. eCollection 2018 Mar 5. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540822 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress in hepatic tissue regeneration by tissue engineering.J Transl Med. 2019 Nov 21;17(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02137-6. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31752920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interconnected Microphysiological Systems for Quantitative Biology and Pharmacology Studies.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 14;8(1):4530. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22749-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29540740 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Organized Liver Microtissue on a Bio-Functional Surface: The Role of Human Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells in Hepatic Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 29;21(13):4605. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134605. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32610471 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
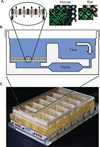
Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:211–324. •• This review describes in detail the approach of designing a 3D organotypic model featured in the current review and presents additional data.
-
-
- Bissell DM, Gores GJ, Laskin DL, Hoofnagle JH. Drug-induced liver injury: mechanisms and test systems. Hepatology. 2001;33:1009–1113. - PubMed
-
- Olson H, Betton G, Robinson D, et al. Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in animals. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2000;32:56–67. - PubMed
-
- Li AP. Accurate prediction of human drug toxicity: a major challenge in drug development. Chem Biol Interact. 2004;150:3–7. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese EJ. Suitability of animal-models for predictive toxicology - theoretical and practical considerations. Drug Metab Rev. 1984;15:505–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
