Interns' knowledge of clinical pharmacology and therapeutics after undergraduate and on-going internship training in Nigeria: a pilot study
- PMID: 19638199
- PMCID: PMC2724475
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-9-50
Interns' knowledge of clinical pharmacology and therapeutics after undergraduate and on-going internship training in Nigeria: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: A sound knowledge of pathophysiology of a disease and clinical pharmacology and therapeutics (CPT) of a drug is required for safe and rational prescribing. The aim of this study was therefore to assess how adequately the undergraduate CPT teaching had prepared interns in Nigeria for safe and rational prescribing and retrospectively, to know how they wanted the undergraduate curriculum to be modified so as to improve appropriate prescribing. The effect of internship training on the prescribing ability of the interns was also sought.
Methods: A total of 100 interns were randomly selected from the Lagos State University Teaching Hospital (LASUTH), Ikeja; Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH), Idiaraba; General Hospital Lagos (GHL); the EKO Hospital, Ikeja; and Havana Specialist Hospital, Surulere. A structured questionnaire was the instrument of study. The questionnaire sought information about the demographics of the interns, their undergraduate CPT teaching, experience of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and drug interactions since starting work, confidence in drug usage and, in retrospect; any perceived deficiencies in their undergraduate CPT teaching.
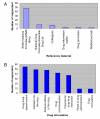
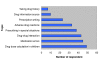
Results: The response rate was 81%. All the respondents graduated from universities in Nigeria. The ability of the interns to prescribe rationally (66, 81.4%) and safely (47, 58%) was provided by undergraduate CPT teaching. Forty two (51.8%) respondents had problems with prescription writing. The interns would likely prescribe antibiotics (71, 87.6%), nonsteroidal analgesics (66, 81.4%), diuretics (55, 67.9%), sedatives (52, 62.9%), and insulin and oral hypoglycaemics (43, 53%) with confidence and unsupervised. The higher the numbers of clinical rotations done, the more confident were the respondents to prescribe unsupervised (chi2 = 19.98, P < 0.001). Similarly, respondents who had rotated through the four major clinical rotations and at least a special posting (chi2 = 11.57, P < 0.001) or four major clinical rotations only (chi2 = 11.25, P < 0.001) were significantly more confident to prescribe drugs unsupervised.
Conclusion: Undergraduate CPT teaching in Nigeria appears to be deficient. Principles of rational prescribing, drug dose calculation in children and pharmacovigilance should be the focus of undergraduate CPT teaching and should be taught both theoretically and practically. Medical students and interns should be periodically assessed on prescribing knowledge and skills during their training as a means of minimizing prescribing errors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Foundation year 1 doctors and clinical pharmacology and therapeutics teaching. A retrospective view in light of experience.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;64(3):363-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02925.x. Epub 2007 May 15. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17506779 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of impact of teaching clinical pharmacology and rational therapeutics to medical undergraduates and interns.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2016 Jul-Sep;6(3):205-10. doi: 10.4103/2229-516X.186967. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27563589 Free PMC article.
-
Do medical courses adequately prepare interns for safe and effective prescribing in New South Wales public hospitals?Intern Med J. 2009 Jul;39(7):428-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.01942.x. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Intern Med J. 2009. PMID: 19383059
-
Do final-year medical students have sufficient prescribing competencies? A systematic literature review.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;84(4):615-635. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13491. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29315721 Free PMC article.
-
Teaching of medical pharmacology: the need to nurture the early development of desired attitudes for safe and rational drug prescribing.Med Teach. 2009 Sep;31(9):847-54. doi: 10.1080/01421590903168119. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19811191 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of modified seminars as a teaching-learning method in pharmacology.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2016 Jul-Sep;6(3):195-200. doi: 10.4103/2229-516X.186971. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27563587 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of providing feedback and prescribing education on prescription writing: An intervention study.Ann Afr Med. 2016 Jan-Mar;15(1):1-6. doi: 10.4103/1596-3519.161722. Ann Afr Med. 2016. PMID: 26857930 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge of adverse drug reaction reporting in first year postgraduate doctors in a medical college.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2012;8:307-12. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S31482. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2012. PMID: 22767994 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the knowledge and attitudes of intern doctors to medication prescribing errors in a Nigeria tertiary hospital.J Basic Clin Pharm. 2013 Dec;5(1):7-14. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.128244. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24808682 Free PMC article.
-
Junior doctors prescribing: enhancing their learning in practice.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;73(2):194-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04061.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21752067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medical and Dental Council of Nigeria Guidelines on minimum standards of medical and dental education in Nigeria. Revised Edition. 1993.
-
- Oshikoya KA, Bello JA, Ayorinde EO. Medical students' view on the methods of teaching pharmacology at the Lagos State University College of Medicine, Nigeria: a need for a change in programme. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 2007;17:101–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources