Cellular and systemic effects of anthrax lethal toxin and edema toxin
- PMID: 19638283
- PMCID: PMC2784088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2009.07.003
Cellular and systemic effects of anthrax lethal toxin and edema toxin
Abstract
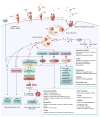
Anthrax lethal toxin (LT) and edema toxin (ET) are the major virulence factors of anthrax and can replicate the lethality and symptoms associated with the disease. This review provides an overview of our current understanding of anthrax toxin effects in animal models and the cytotoxicity (necrosis and apoptosis) induced by LT in different cells. A brief reexamination of early historic findings on toxin in vivo effects in the context of our current knowledge is also presented.
References
-
- Alam S, Gupta M, Bhatnagar R. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by anthrax edema toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;339:107–114. - PubMed
-
- Alfano RW, Leppla SH, Liu S, Bugge TH, Duesbery NS, Frankel AE. Potent inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by the matrix metalloproteinase-activated anthrax lethal toxin: Implications for broad anti-tumor efficacy. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:745–749. - PubMed
-
- Alileche A, Squires RC, Muehlbauer SM, Lisanti MP, Brojatsch J. Mitochondrial impairment is a critical event in anthrax lethal toxin-induced cytolysis of murine macrophages. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:100–106. - PubMed
-
- Banks DJ, Barnajian M, Maldonado-Arocho FJ, Sanchez AM, Bradley KA. Anthrax toxin receptor 2 mediates Bacillus anthracis killing of macrophages following spore challenge. Cell Microbiol. 2005;7:1173–1185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources