The novel distribution of phosphodiesterase-4 subtypes within the rat retina
- PMID: 19638302
- PMCID: PMC2774823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.045
The novel distribution of phosphodiesterase-4 subtypes within the rat retina
Abstract
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are important regulators of signal transduction processes. While much is known about the function of cyclic GMP-specific PDEs in the retina, much less is known about the closely related, cyclic AMP-specific PDEs. The purpose of the present study is to characterize and localize PDE4 within the adult rat retina. We have used Western blotting, RT-PCR, and immunohistochemistry together with retrograde labeling to determine the presence and location of each PDE4 subtype. Western blot analysis revealed that multiple isoforms of PDE4A, B, and D subtypes are present within the retina, whereas the PDE4C subtype was absent. These data were confirmed by RT-PCR. Using immunohistochemistry we show that all three PDE4s are abundantly expressed within the retina where they all colocalize with retrograde-labeled retinal ganglion cells, as well as bipolar cells, horizontal cells, and cholinergic amacrine cells, whereas Müller cells lack PDE4 expression. Uniquely, PDE4B was expressed by the inner and outer segments of rod photoreceptors as well as their terminals within the outer plexiform layer. Collectively, our results demonstrate that PDE4s are abundantly expressed throughout the rodent retina and this study provides the framework for further functional studies.
Figures
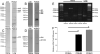



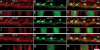





Similar articles
-
Challenge of human Jurkat T-cells with the adenylate cyclase activator forskolin elicits major changes in cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) expression by up-regulating PDE3 and inducing PDE4D1 and PDE4D2 splice variants as well as down-regulating a novel PDE4A splice variant.Biochem J. 1997 Jan 1;321 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):165-75. doi: 10.1042/bj3210165. Biochem J. 1997. PMID: 9003416 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression and protein localization of calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase in adult rat retina.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Oct;84(5):1020-6. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21009. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16881052
-
Expression and distribution of phosphodiesterase isoenzymes in the human seminal vesicles.J Sex Med. 2011 Nov;8(11):3058-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02397.x. Epub 2011 Aug 2. J Sex Med. 2011. PMID: 21810184
-
cAMP-Specific phosphodiesterase-4 enzymes in the cardiovascular system: a molecular toolbox for generating compartmentalized cAMP signaling.Circ Res. 2007 Apr 13;100(7):950-66. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000261934.56938.38. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17431197 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterases in neurodegenerative disorders.IUBMB Life. 2012 Dec;64(12):965-70. doi: 10.1002/iub.1104. Epub 2012 Nov 5. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 23129425 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Roles of cAMP in Vertebrate Retina.Cells. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):1157. doi: 10.3390/cells12081157. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs in human and vertebrate neural retinas.RNA Biol. 2019 Jun;16(6):821-829. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1591034. Epub 2019 Apr 2. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 30874468 Free PMC article.
-
Histological Evaluation of Diabetic Neurodegeneration in the Retina of Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rats.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 21;7(1):8891. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09068-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28827737 Free PMC article.
-
The sleep quality- and myopia-linked PDE11A-Y727C variant impacts neural physiology by reducing catalytic activity and altering subcellular compartmentalization of the enzyme.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 17:2023.11.16.567422. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.16.567422. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cells. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):2839. doi: 10.3390/cells12242839. PMID: 38014312 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dominant-Negative Attenuation of cAMP-Selective Phosphodiesterase PDE4D Action Affects Learning and Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 9;21(16):5704. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165704. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Majid RM, Tremblay F, Baldridge WH. Localization of adenylyl cyclase proteins in the rodent retina. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;101:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed T, Frey JU. Expression of the specific type IV phosphodiesterase gene PDE4B3 during different phases of long-term potentiation in single hippocampal slices of rats in vitro. Neuroscience. 2003;117:627–638. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed T, Frey S, Frey JU. Regulation of the phosphodiesterase PDE4B3-isotype during long-term potentiation in the area dentata in vivo. Neuroscience. 2004;124:857–867. - PubMed
-
- Ariga M, Neitzert B, Nakae S, Mottin G, Bertrand C, Pruniaux MP, Jin SL, Conti M. Nonredundant function of phosphodiesterases 4D and 4B in neutrophil recruitment to the site of inflammation. J Immunol. 2004;173:7531–7538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

