The green tea polyphenol EGCG potentiates the antiproliferative activity of c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 19638461
- PMCID: PMC4299643
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0109
The green tea polyphenol EGCG potentiates the antiproliferative activity of c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
Purpose: Activation of the c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) promotes the growth and survival of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Specific receptor antagonists have shown efficacy in the clinic, but tumors often become resistant to these therapies. We investigated the ability of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) to inhibit cell proliferation, and c-Met receptor and EGFR kinase activation in several NSCLC cell lines.
Experimental design: NSCLC cell lines with variable sensitivity to the EGFR antagonist erlotinib were studied. Cell growth was evaluated using proliferation and colony formation assays. Kinase activation was assessed via Western blot analysis. Experiments were conducted with EGCG, the EGFR antagonist erlotinib, and the c-Met inhibitor SU11274. The antagonists were also tested in a xenograft model using SCID mice.
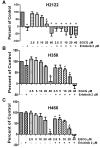
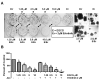
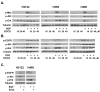
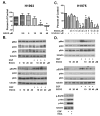
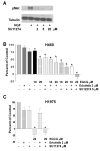
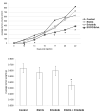
Results: EGCG inhibited cell proliferation in erlotinib-sensitive and -resistant cell lines, including those with c-Met overexpression, and acquired resistance to erlotinib. The combination of erlotinib and EGCG resulted in greater inhibition of cell proliferation and colony formation than either agent alone. EGCG also completely inhibited ligand-induced c-Met phosphorylation and partially inhibited EGFR phosphorylation. The triple combination of EGCG/erlotinib/SU11274 resulted in a greater inhibition of proliferation than EGCG with erlotinib. Finally, the combination of EGCG and erlotinib significantly slowed the growth rate of H460 xenografts.
Conclusion: EGCG is a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation, independent of EGFR inhibition, in several NSCLC cell lines, including those resistant to both EGFR kinase inhibitors and those overexpressing c-Met. Therefore, EGCG might be a useful agent to study as an adjunct to other anticancer agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors express no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibition of head and neck tumor growth by green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor.Int J Cancer. 2008 Sep 1;123(5):1005-14. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23585. Int J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18546267 Free PMC article.
-
Combined therapy with mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor and Met kinase inhibitor for overcoming erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Oct;11(10):2149-57. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0195. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22844075
-
Synergistic effect of afatinib with su11274 in non-small cell lung cancer cells resistant to gefitinib or erlotinib.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059708. Epub 2013 Mar 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527257 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative signaling pathways as potential therapeutic targets for overcoming EGFR and c-Met inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4;8(11):e78398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078398. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223799 Free PMC article.
-
Dual MET-EGFR combinatorial inhibition against T790M-EGFR-mediated erlotinib-resistant lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2008 Sep 16;99(6):911-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604559. Br J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 19238632 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Preventive and therapeutic effects of green tea on lung cancer: a narrative review of evidence from clinical and basic research.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Dec;14(12):5029-5038. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1791. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36647481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of natural phenolic compounds for the potential treatment of lung cancer.Daru. 2019 Jun;27(1):433-449. doi: 10.1007/s40199-019-00267-2. Epub 2019 May 21. Daru. 2019. PMID: 31115871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGCG reverses human neutrophil elastase-induced migration in A549 cells by directly binding to HNE and by regulating α1-AT.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 16;5:11494. doi: 10.1038/srep11494. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26177797 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic inhibition of lung cancer cells by EGCG and NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7082.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 21;10(26):6543-6556. doi: 10.7150/jca.34285. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31777584 Free PMC article.
-
A derivative of epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis via SHP-1-mediated suppression of BCR-ABL and STAT3 signalling in chronic myelogenous leukaemia.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;172(14):3565-78. doi: 10.1111/bph.13146. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25825203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–81. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Haber DA. Molecular predictors of response to epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:587–95. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, et al. TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5892–9. - PubMed
-
- Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A, et al. Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1545–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

