Primary graft function, metabolic control, and graft survival after islet transplantation
- PMID: 19638525
- PMCID: PMC2713623
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-1685
Primary graft function, metabolic control, and graft survival after islet transplantation
Abstract
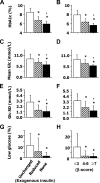
OBJECTIVE To investigate the influence of primary graft function (PGF) on graft survival and metabolic control after islet transplantation with the Edmonton protocol. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS A total of 14 consecutive patients with brittle type 1 diabetes were enrolled in this phase 2 study and received median 12,479 islet equivalents per kilogram of body weight (interquartile range 11,072-15,755) in two or three sequential infusions within 67 days (44-95). PGF was estimated 1 month after the last infusion by the beta-score, a previously validated index (range 0-8) based on insulin or oral treatment requirements, plasma C-peptide, blood glucose, and A1C. Primary outcome was graft survival, defined as insulin independence with A1C < or =6.5%. RESULTS All patients gained insulin independence within 12 days (6-23) after the last infusion. PGF was optimal (beta-score > or =7) in nine patients and suboptimal (beta-score < or =6) in five. At last follow-up, 3.3 years (2.8-4.0) after islet transplantation, eight patients (57%) remained insulin independent with A1C < or =6.5%, including seven patients with optimal PGF (78%) and one with suboptimal PGF (20%) (P = 0.01, log-rank test). Graft survival was not significantly influenced by HLA mismatches or by preexisting islet autoantibodies. A1C, mean glucose, glucose variability (assessed with continuous glucose monitoring system), and glucose tolerance (using an oral glucose tolerance test) were markedly improved when compared with baseline values and were significantly lower in patients with optimal PGF than in those with suboptimal PGF. CONCLUSIONS Optimal PGF was associated with prolonged graft survival and better metabolic control after islet transplantation. This early outcome may represent a valuable end point in future clinical trials.
Figures

Comment in
-
Improvement of electrophysiological neuropathy after islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes: a 5-year prospective study.Diabetes Care. 2014 Jun;37(6):e141-2. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0320. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24855172 No abstract available.
References
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, Secchi A, Brendel MD, Berney T, Brennan DC, Cagliero E, Alejandro R, Ryan EA, DiMercurio B, Morel P, Polonsky KS, Reems JA, Bretzel RG, Bertuzzi F, Froud T, Kandaswamy R, Sutherland DE, Eisenbarth G, Segal M, Preiksaitis J, Korbutt GS, Barton FB, Viviano L, Seyfert-Margolis V, Bluestone J, Lakey JR: International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1318– 1330 - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, Lakey JR, Shapiro AM: Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2060– 2069 - PubMed
-
- Froud T, Ricordi C, Baidal DA, Hafiz MM, Ponte G, Cure P, Pileggi A, Poggioli R, Ichii H, Khan A, Ferreira JV, Pugliese A, Esquenazi VV, Kenyon NS, Alejandro R: Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes mellitus using cultured islets and steroid-free immunosuppression: Miami experience. Am J Transplant 2005; 5: 2037– 2046 - PubMed
-
- Gerber PA, Pavlicek V, Demartines N, Zuellig R, Pfammatter T, Wuthrich R, Weber M, Spinas GA, Lehmann R: Simultaneous islet-kidney vs pancreas-kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a 5 year single centre follow-up. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 110– 119 - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Islet Transplantation Registry Annual Report Rockville, Maryland, The EMMES Corporation, 2007
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

