Cancellation of EEG and MEG signals generated by extended and distributed sources
- PMID: 19639553
- PMCID: PMC2797557
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20851
Cancellation of EEG and MEG signals generated by extended and distributed sources
Abstract
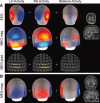
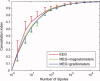
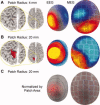
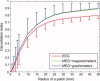
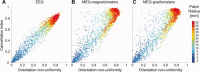
Extracranial patterns of scalp potentials and magnetic fields, as measured with electro- and magnetoencephalography (EEG, MEG), are spatially widespread even when the underlying source in the brain is focal. Therefore, loss in signal magnitude due to cancellation is expected when multiple brain regions are simultaneously active. We characterized these cancellation effects in EEG and MEG using a forward model with sources constrained on an anatomically accurate reconstruction of the cortical surface. Prominent cancellation was found for both EEG and MEG in the case of multiple randomly distributed source dipoles, even when the number of simultaneous dipoles was small. Substantial cancellation occurred also for locally extended patches of simulated activity, when the patches extended to opposite walls of sulci and gyri. For large patches, a difference between EEG and MEG cancellation was seen, presumably due to selective cancellation of tangentially vs. radially oriented sources. Cancellation effects can be of importance when electrophysiological data are related to hemodynamic measures. Furthermore, the selective cancellation may be used to explain some observed differences between EEG and MEG in terms of focal vs. widespread cortical activity.
2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlfors SP, Simpson GV ( 2004): Geometrical interpretation of fMRI‐guided MEG/EEG inverse estimates. Neuroimage 22: 323–332. - PubMed
-
- Ahonen AI, Hamalainen MS, Ilmoniemi RJ, Kajola MJ, Knuutila JE, Simola JT, Vilkman VA ( 1993): Sampling theory for neuromagnetic detector arrays. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40: 859–869. - PubMed
-
- Baillet S, Mosher JC, Leahy RM ( 2001): Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE Signal Proc Mag 18: 14–30.
-
- Cohen D, Cuffin BN ( 1983): Demonstration of useful differences between magnetoencephalogram and electroencephalogram. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 56: 38–51. - PubMed
-
- Cohen D, Halgren E ( 2009): Magnetoencephalography In: Squire LR, editor. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, Vol. 5, pp. 615–622. Oxford: Academic Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NS18741/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS44623/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB07298/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB001680/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS37462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS018741/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB007298/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD040712/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR14075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057500/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS57500/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DA14178/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044623/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS037462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD40712/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS057500/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014178/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

