Circularly polarized luminescence in enantiopure europium and terbium complexes with modular, all-oxygen donor ligands
- PMID: 19639983
- PMCID: PMC2735592
- DOI: 10.1021/ic901079s
Circularly polarized luminescence in enantiopure europium and terbium complexes with modular, all-oxygen donor ligands
Abstract
The modular syntheses of three new octadentate, enantiopure ligands are reported, one with the bidentate chelating unit 2-hydroxyisophthalamide (IAM) and two with bidentate 1-hydroxy-2-pyridinone (1,2-HOPO) units. A new design principle is introduced for the chiral, non-racemic hexamines which constitute the central backbones for the presented class of ligands. The terbium(III) complex of the IAM ligand, as well as the europium(III) complexes of the 1,2-HOPO ligands, are synthesized and characterized by various techniques (NMR, UV, CD, luminescence spectroscopy). All species exhibit excellent stability and moderate to high luminescence efficiency (quantum yields Phi(Eu) = 0.05-0.08 and Phi(Tb) = 0.30-0.57) in aqueous solution at physiological pH. Special focus is put onto the properties of the complexes in regard to circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). The maximum luminescence dissymmetry factors (g(lum)) in aqueous solution are high with |g(lum)|(max) = 0.08-0.40. Together with the very favorable general properties (good stability, high quantum yields, long lifetimes), the presented lanthanide complexes can be considered as good candidates for analytical probes based on CPL in biologically relevant environments.
Figures
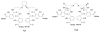










References
-
- Lakowicz JR. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Springer; Berlin: 2006.
- Wolfbeis OS, editor. Fluorescence Spectroscopy: New Methods and Applications. Springer; Berlin: 1993.
-
-
Selected reviews: Parker D. Chem Soc Rev. 2004;33:156–165.Bünzli JCG, Piguet C. Chem Soc Rev. 2005;34:1048–1077.Bünzli JCG. Acc Chem Res. 2006;39:53–61.de Bettencourt-Dias A. Curr Org Chem. 2007;11:1460–1480.Gunnlaugsson T, Stomeo F. Org Biomol Chem. 2007;5:1999–2009.Bünzli JCG. Chem Lett. 2009;38:104–109.Montgomery CP, Murray BS, New EJ, Pal R, Parker D. Acc Chem Res ASAP. doi: 10.1021/ar800174z.
-
-
-
For example: Perkin-Elmer: Delfia and LANCE, Cisbio: HTRF and Lumi4, Brahms: TRACE.
-
-
-
Reviews: Richardson FS, Riehl JP. Chem Rev. 1977;77:773–792.Riehl JP, Richardson FS. Chem Rev. 1986;86:1–16.Riehl JP, Richardson FS. Methods Enzymol. 1993;226:539–553.Brittain HG. Appl Spectr Rev. 2000;35:175–201.Dekkers HPJM. In: Circular Dichroism. Berova N, Nakanishi K, Woody RW, editors. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 2000. Riehl JP, Muller G. In: Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths. Gschneidner KA, Bünzli J-CG, Pecharsky VK, editors. Vol. 34. North-Holland Publishing; Amsterdam: 2005.
-
-
- Dickins RS, Howard JAK, Maupin CL, Moloney JM, Parker D, Riehl JP, Siligardi G, Williams JAG. Chem Eur J. 1999;5:1095–1105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

