Generation and analysis of a 29,745 unique Expressed Sequence Tags from the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) assembled into a publicly accessible database: the GigasDatabase
- PMID: 19640306
- PMCID: PMC2907693
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-341
Generation and analysis of a 29,745 unique Expressed Sequence Tags from the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) assembled into a publicly accessible database: the GigasDatabase
Abstract
Background: Although bivalves are among the most-studied marine organisms because of their ecological role and economic importance, very little information is available on the genome sequences of oyster species. This report documents three large-scale cDNA sequencing projects for the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas initiated to provide a large number of expressed sequence tags that were subsequently compiled in a publicly accessible database. This resource allowed for the identification of a large number of transcripts and provides valuable information for ongoing investigations of tissue-specific and stimulus-dependant gene expression patterns. These data are crucial for constructing comprehensive DNA microarrays, identifying single nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellites in coding regions, and for identifying genes when the entire genome sequence of C. gigas becomes available.
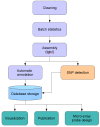
Description: In the present paper, we report the production of 40,845 high-quality ESTs that identify 29,745 unique transcribed sequences consisting of 7,940 contigs and 21,805 singletons. All of these new sequences, together with existing public sequence data, have been compiled into a publicly-available Website http://public-contigbrowser.sigenae.org:9090/Crassostrea_gigas/index.html. Approximately 43% of the unique ESTs had significant matches against the SwissProt database and 27% were annotated using Gene Ontology terms. In addition, we identified a total of 208 in silico microsatellites from the ESTs, with 173 having sufficient flanking sequence for primer design. We also identified a total of 7,530 putative in silico, single-nucleotide polymorphisms using existing and newly-generated EST resources for the Pacific oyster.
Conclusion: A publicly-available database has been populated with 29,745 unique sequences for the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. The database provides many tools to search cleaned and assembled ESTs. The user may input and submit several filters, such as protein or nucleotide hits, to select and download relevant elements. This database constitutes one of the most developed genomic resources accessible among Lophotrochozoans, an orphan clade of bilateral animals. These data will accelerate the development of both genomics and genetics in a commercially-important species with the highest annual, commercial production of any aquatic organism.
Figures


References
-
- Cunningham C, Hikima J, Jenny MJ, Chapman RW, Fang GC, Saski C, Lundqvist ML, Wing RA, Cupit PM, Gross PS. et al. New resources for marine genomics: bacterial artificial chromosome libraries for the Eastern and Pacific oysters (Crassostrea virginica and C. gigas) Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2006;8(5):521–533. doi: 10.1007/s10126-006-6013-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saavedra C, Bachère E. Bivalve genomics. Aquaculture. 2006;256(1–4):1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.02.023. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

